S.O.V.A. - A new Android Banking trojan with fowl intentions
09 September 2021

Jump to
Intro
In the beginning of August 2021, during our daily threat hunting, ThreatFabric researchers came across a new Android banking trojan. Based on the login panel of the C2 server, we could see that it was called S.O.V.A. by its own creators.
Sova is the Russian word for owl. This name was chosen by the threat actor himself/herself possibly because of owl’s nature as nocturnal birds of prey, quiet but efficient in stalking and capturing their victims. This identifies a completely new, to the best of our knowledge, Android banking trojan. The trojan is currently in development and testing phase, and has the objective to add to his overlay and keylogging mechanisms, other higly dangerous features like DDoS and Ransomware in future versions. There are a few interesting aspects that differentiate this trojan to already existing ones, both in features as well as in development.
S.O.V.A. contains features that are usually available in current Android malware, including:
- Overlay attacks;
- Keylogging;
- Notification manipulation.
In addition, it stands out for a feature that is not as common in Android malware:
- Session cookies theft
This functionality allows the criminals to have access to valid logged in sessions from the users without the need of knowing the banking credentials.
Regardless, this malware is still in its infancy and it is undergoing a testing phase at the time of writing, prospecting serious and worrying plans for the near future. This observation is confirmed by a message from its author(s) posted on hacking forums.
The author publicly advertises for trial of this new product - targeting a large number of banks - looking to improve the bot’s functionalities, and test on a large variety of mobile devices. In addition to testing, the authors have established a clear roadmap of future features to be implemented in the malware.
Like many others, S.O.V.A. is also taking a page out of traditional desktop malware, confirming a trend that has been existing for the past few years in mobile malware. Including DDoS, Man in the Middle, and Ransomware to its arsenal could mean incredible damage to end users, in addition to the already very dangerous threat that overlay and keylogging attacks serve.
Regarding the development, S.O.V.A. also stands out for being fully developed in Kotlin, a coding language supported by Android and thought by many to be the future of Android development. If the author promises on future features are kept, S.O.V.A. could potentially be the most complete and advanced Android bot to be fully developed in Kotlin to this day.
NOTE: Just one day before the publishing of this blog, two new versions of S.O.V.A. were found in the wild. The new versions do not change radically from the original, but do introduce some new features and commands. In the following analysis, the additions brought by the newer version of the malware will be tagged with a (v2) and (v3) symbols.
A ‘Updates’ section was added at the end of the blog to sum up the new features added.
Context
Currently, ThreatFabric identified five samples of S.O.V.A. in the wild, with a total of three different malware versions.
The following screenshot contains the VirusTotal page for the obfuscated and packed version of S.O.V.A..
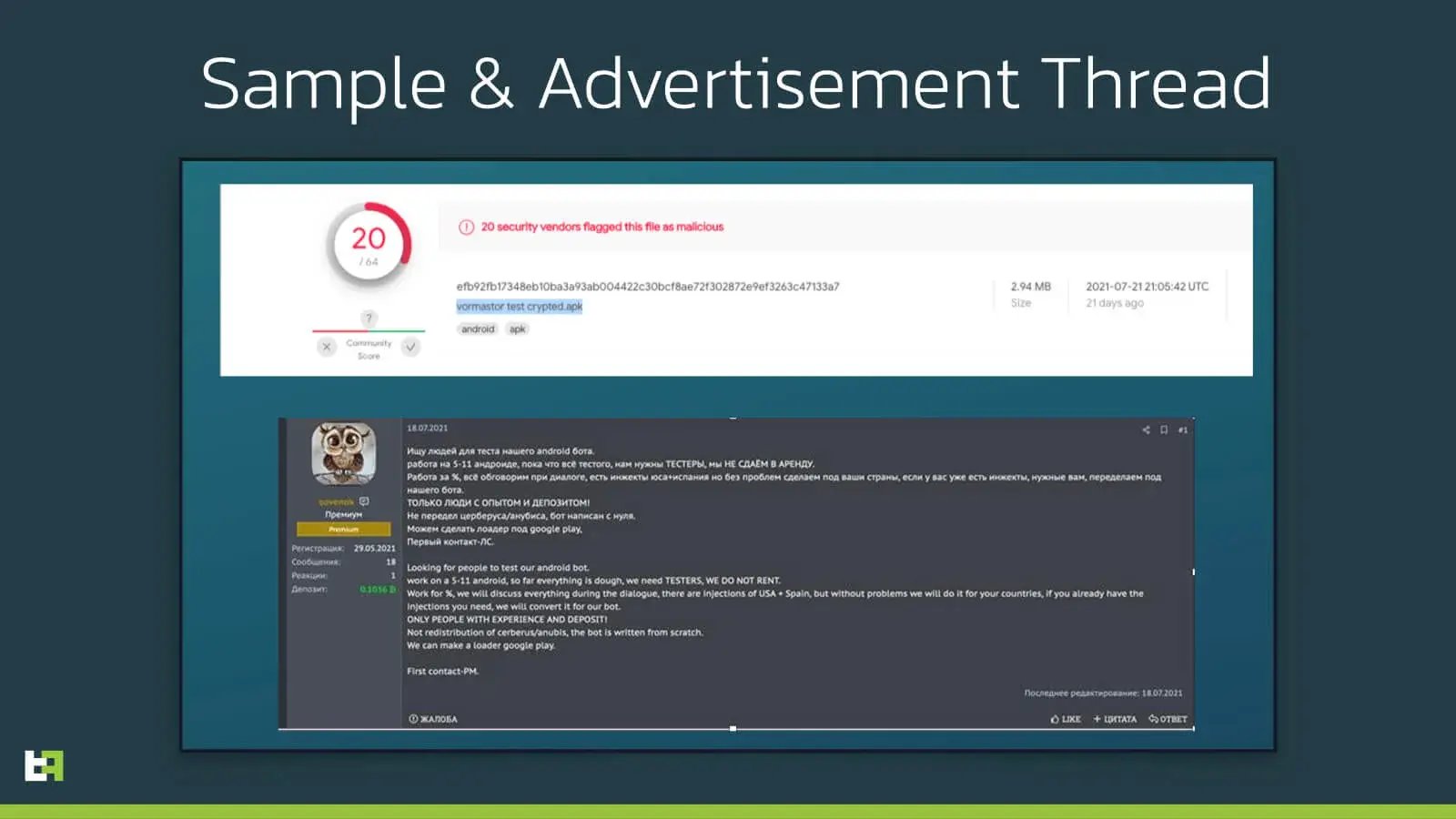
The string highlighted, underneath the file’s hash, is the name the file was uploaded to VirusTotal with. The file name is ‘vormastor test crypted.apk’. As mentioned in the introduction, we conclude that this malware family is still in its testing phase and has been for a few weeks. This is confirmed by a post by the author and seller of S.O.V.A., who was already looking for testers at the end of July.
At the beginning of September, this same user published the first post aimed at selling the bot. In the same thread, the seller is being criticized by other members for having Russian banks within the list of targets. From this thread it also seems that the future versions of this Android malware could switch back to Java, to address some compatibility issues with the obfuscation software they are using.
According to the authors, there are already mutiple overlays available for different banking institutions from the USA and Spain, but they offer the possibility of creating more in case of necessity from the buyer.
Commands
The main objective of S.O.V.A. is to gather the victim’s PII.
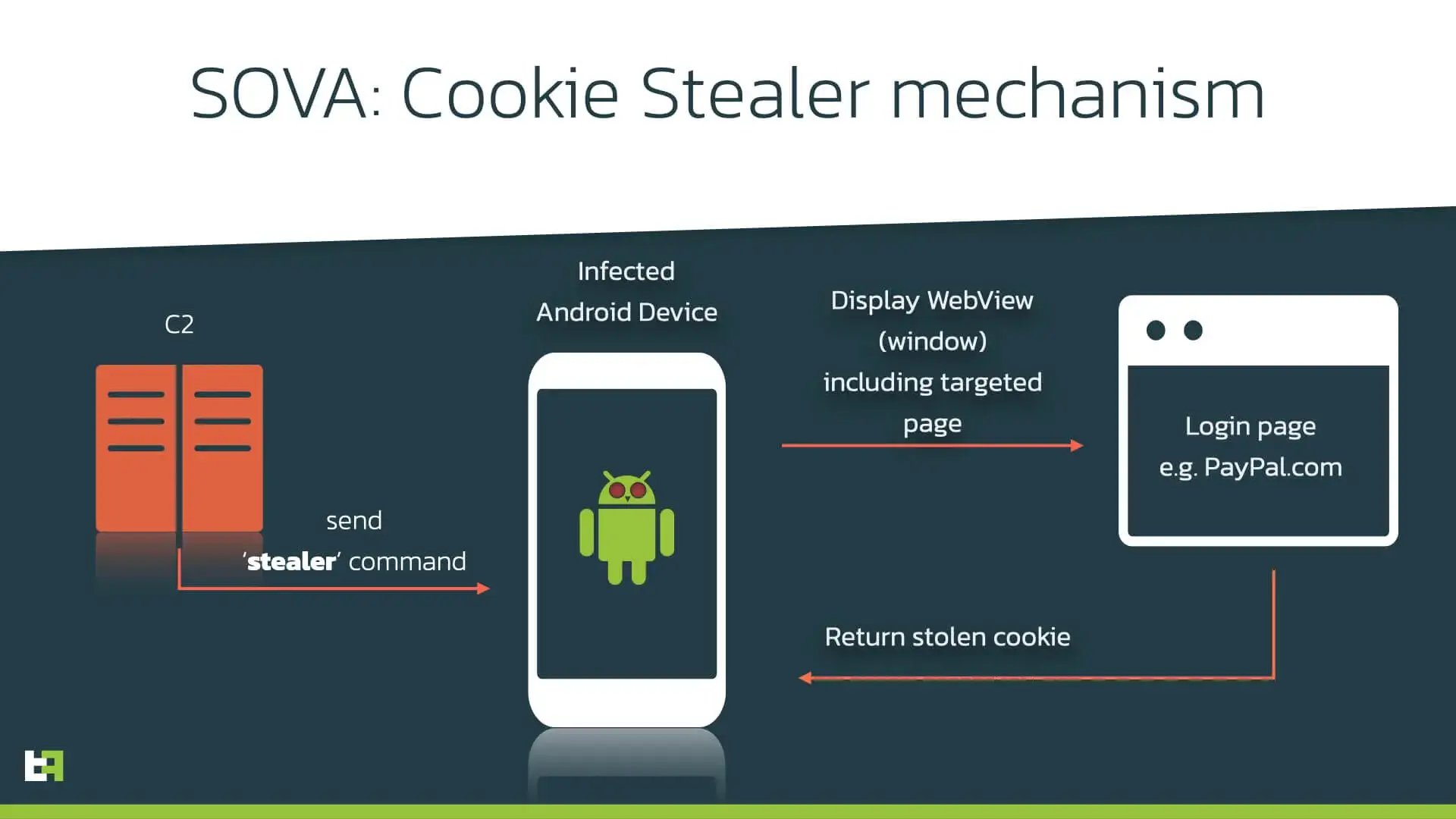
S.O.V.A. tries its best to remain undetected. To achieve this, S.O.V.A. abuses the overlay mechanic to trick victims into revealing their passwords, and other important private information. In an overlay attack, users type their credentials in what they think is a legitimate banking app, effectively giving them to a page controlled by the attacker. S.O.V.A. also has the possibility to steal session cookies from the device. This feature is not unheard of but is definitely not common on modern Android Trojans.
Like most of the banking trojans, S.O.V.A. heavily relies on Accessibility Services. When it is started for the first time, the malware hides its app icon and abuses the Accessibility Services to obtain all the necessary permissions to operate properly.
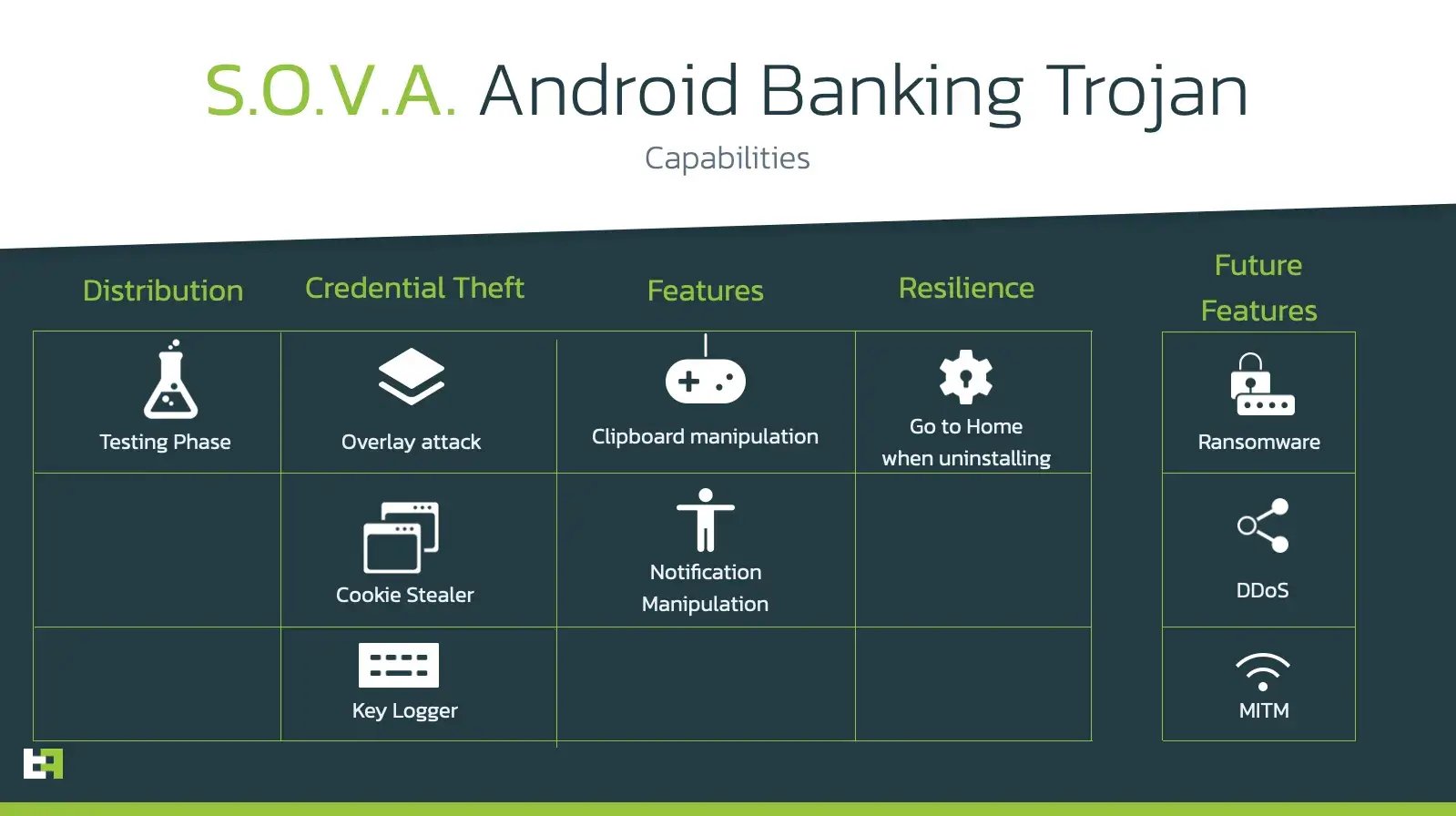
Functionalities of the bot, as advertised by its authors, include:
- Steal Device Data.
- Send SMS.
- Overlay and Cookie injection.
- Overlay and Cookie injection via Push notification.
- USSD execution.
- Credit Card overlays with validity check.
- Hidden interception for SMS.
- Hidden interception for Notifications.
- Keylogger.
- Uninstallation of the app.
- Resilience from uninstallation from victims.
The features that S.O.V.A. offers are in line with the standard for Android malware that we are used to see in 2021. However, as previously mentioned, the criminals behind this bot are very proactive and have also released a detailed roadmap of the features to be included in the future releases of S.O.V.A.:
- Automatic 3 stage overlay injections.
- Automatic cookie injections.
- Clipboard manipulation.
- DDoS
- Improved Panel Health.
- Ransomware (with overlay for card number).
- Man in the Middle (MitM).
- Normal Push notifications.
- More overlays.
- VNC.
- 2FA interception.
It is very interesting to note how this group has a roadmap for their product, including a phase with early adopters to test the bot and the infrastructure. The second set of features, added in the future developments, are very advanced and would push S.O.V.A. into a different realm for Android banking malware. If speculations will become real, it will make S.O.V.A. potentially one of the most advanced bots in circulation combining banking malware with automation and botnet capabilities.
Nonetheless, this behavior indicates that the authors have a lot of ambitions regarding this malware, making it a very dangerous threat for the Android banking ecosystem.
Commands list
The following list includes all the commands that can be send by the C2 to the bot:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| startddos | Start DDoS service |
| stealer | Steal session cookie of specific app |
| hidensms | Hide received SMS |
| starthidenpush | Hide push notifications |
| delbot | Delete the bot from device |
| getlog | Send key logged data |
| startkeylog | Clears key logged data |
| scaninject | Adds new injects to injects list |
| stopkeylog | Same as startkeylog |
| openinject | Open WebView with link provided |
| stophidenpush | Stop hiding push notifications |
| sendpush | Display Push notification to start WebView Injection |
| stophidensms | Stops hiding received SMS |
| stopddos | Stop DDoS service |
| stopscan | Stops injects |
| stealerpush | Same as sendpush |
| sendsms | Send SMS |
| scancookie | Adds package to cookie stealing list (v2) |
| stopcookie | Removes package names from cookie stealing list (v2) |
| get2fa | Obtains 2 factor Authentications tokes from Google Authenticatos (v3) |
As expected, not all the commands function properly, a few are not implemented fully or are copies of existing ones. This can be a result of the bot being still in the testing and development phase.
Capabilities
Here is a brief description of the main and most interesting functionalities of S.O.V.A.
Overlay Attack
Like the large majority of Android banking trojans, S.O.V.A. relies on Overlay attacks to steal PII from its victims. If the user is trying to access a banking application included in S.O.V.A.’s active target list, the malware will be notified with Accessibility Services, and will display a WebView overlay posing as the intended banking application.
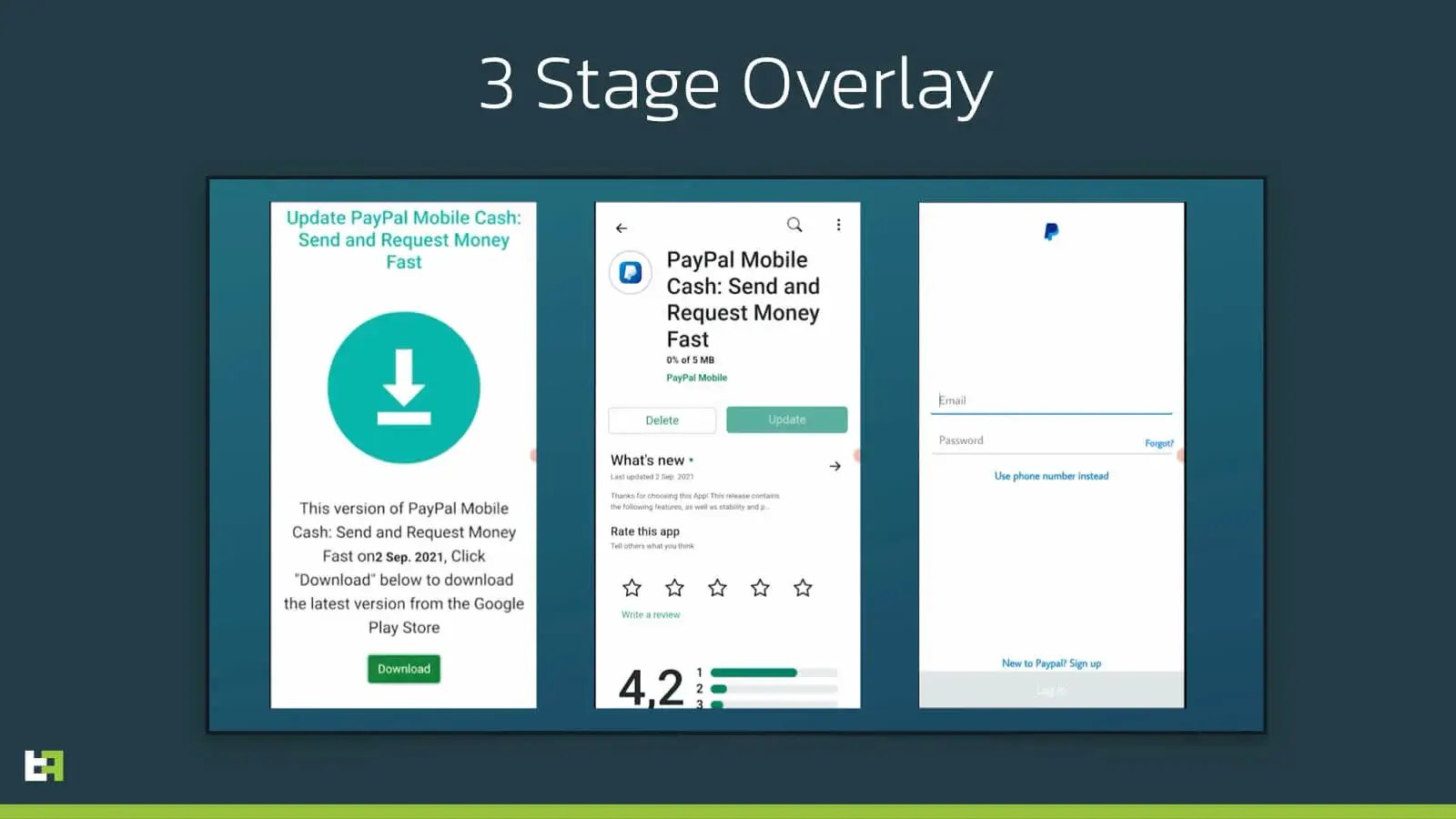
In addition, the author claims that future S.O.V.A. releases will have what a so-called 3-stage-overlay. In the screenshots below you can see a demonstration of this 3-stage-overlay, taken from a demonstration video released in early September by the criminals themselves. It is not clear what the 3 stages imply, but it could mean more advances and realistic process, maybe implying download of additional software to the device.
The target list is contained in an asset file called ‘packageList.txt’. This list is quite extensive, and contains banking applications, cryptocurrency wallets, and shopping applications that require credit card access to operate.
In the following graph you can observe the country distribution of the targets:
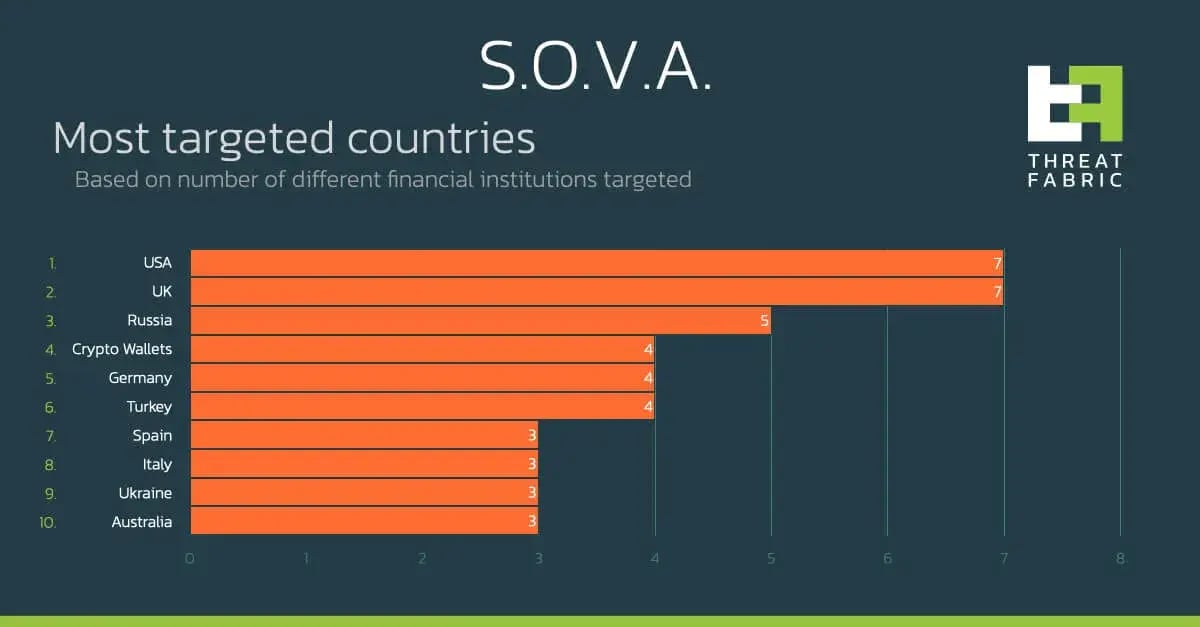
As mentioned before, the authors declared in their online advertisement that at the moment they only have mobile banking overlays for banks Spain and USA, but as we have seen before with many other Android banking trojans, it is very easy for criminals to add new overlays in a very short amount of time.
Session Stealer
Another interesting feature of S.O.V.A., which is uncommon in Android malware, is the ability to steal cookies. Cookies are a vital part of web functionality, which allow users to maintain open sessions on their browsers without having to re-input their credentials repeatedly. A malicious actor in possession on a valid session cookie has effectively access to the victim’s logged in web session.
S.O.V.A. will create a WebView to open a legitimate web URL for the target application and steal the cookies once the victim successfully logs in, using the Android CookieManager.
The following code fragment shows how the overlay WebView is created:
this.setContentView(0x7F070001); // layout:activity_web_view
WebView v1 = (WebView) this.a(0x7F05001D); // id:web_view
Checks.checkNotNullWithName(v1, "web_view");
WebSettings webSettings = v1.getSettings();
Checks.checkNotNullWithName(webSettings, "web_view.settings");webSettings.setJavaScriptEnabled(true);((WebView) this.a(0x7F05001D)).setLayerType(2, null);
// id:web_viewString
link = this.getIntent().getStringExtra("link");boolean getCookieFlag = this.getIntent().getBooleanExtra("getCookie", false);CookieManager cookieManager = CookieManager.getInstance();CookieSyncManager.createInstance(this.getApplicationContext());cookieManager.setAcceptThirdPartyCookies(((WebView) this.a(0x7F05001D)), true);
// id:web_viewcookieManager.acceptCookie();
CookieSyncManager.getInstance().startSync();WebView webView2 = (WebView) this.a(0x7F05001D);
// id:web_viewChecks.checkNotNullWithName(webView2, "web_view");
Checks.checkNotNullWithName(cookieManager, "cookieManager");webView2.setWebViewClient(new CustomWebViewClient(this, ((boolean)(((int) getCookieFlag))), cookieManager));if (link != null) { ((WebView) this.a(0x7F05001D)).loadUrl(link);
// id:web_view
}The malware does not require specific permissions to run this code, and ThreatFabric has confirmed that it is capable of stealing session cookies from major websites like Gmail or PayPal with ease. In the newer version of S.O.V.A., criminals added the option to create a list of applications to monitor for cookies automatically.
DDoS
DDoS stands for Distributed Denial of Service. It is a type of attack whose objective is to exhaust the resources of a device to make it unavailable to its intended users. Based on the advertisement post, this feature is a work in progress and will be available in the future. S.O.V.A. is not the first malware to incorporate DDoS capabilities, but it is an uncommon feature in the current Android malware ecosystem.
Despite being part of the features to be released, the bot has a startddos command, that will execute the following code, within a Kotlin coroutine:
do {
retrofitManager v3 = this.mRetrofitManager;
if (!v3.isActive) {
return l.a;
}
Objects.requireNonNull(v3.retrofitClient);
this.i = v1_1;
this.j = 1;
}
while (retrofitClient.ddosEndpoint.request(this.link, this) != v0);Currently, this functionality is listed by the authors as a work in progress. Despite this, the bot is actually able to create requests for the given URL using RetroFit.
RetroFitBuilder DDOSretroFitBuilder = new RetroFitBuilder();
DDOSretroFitBuilder.setHTTPClient(okHTTPClient);
DDOSretroFitBuilder.setBaseUrl("http://google.com/");
myConverterFactory DDoSConverterFactory = myConverterFactory.c();
DDOSretroFitBuilder.converterFactories.add(DDoSConverterFactory);
retrofitClient.ddosEndpoint = (ddosEndpoint)DDOSretroFitBuilder.buildRetrofit().getProxyClass(ddosEndpoint.class);
Despite setting ‘google.com’ as base URL, by using the @Url annotation from RetroFit, the authors are able to dynamically input a completely new URL. As DDoS is not listed in the bot capabilities, it is likely that the criminals do not fully trust this implementation to consider it a complete feature yet.
Clipper & Cryptocurreny wallets
Another feature that is incorporated in S.O.V.A., that we observed in other malware like Medusa, is the ability of altering the data in the system clipboard. The bot sets up an event listener, designed to notify the malware whenever some new data is saved in the clipboard. If the string of data is potentially a cryptocurrency wallet address, S.O.V.A. substitutes it with a valid address for the corresponding cryptocurrency.
The supported cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, Ethereum, Binance coin, and TRON. The relative addresses can be found in the IOC section. The following code snippet shows the checks for Binance Coin:
String v1 = v0.substring(0, 3);
Checks.checkNotNullWithName2(v1, "(this as java.lang.Strin…ing(startIndex, endIndex)");
if (Checks.nullOrEqual(v1, "bnb")) {
this.b.setText(clipboardManager.bnbAddress);
}Currently, the corresponding wallets are either empty or almost empty. Here in the following image, you can see the Bitcoin related wallet:
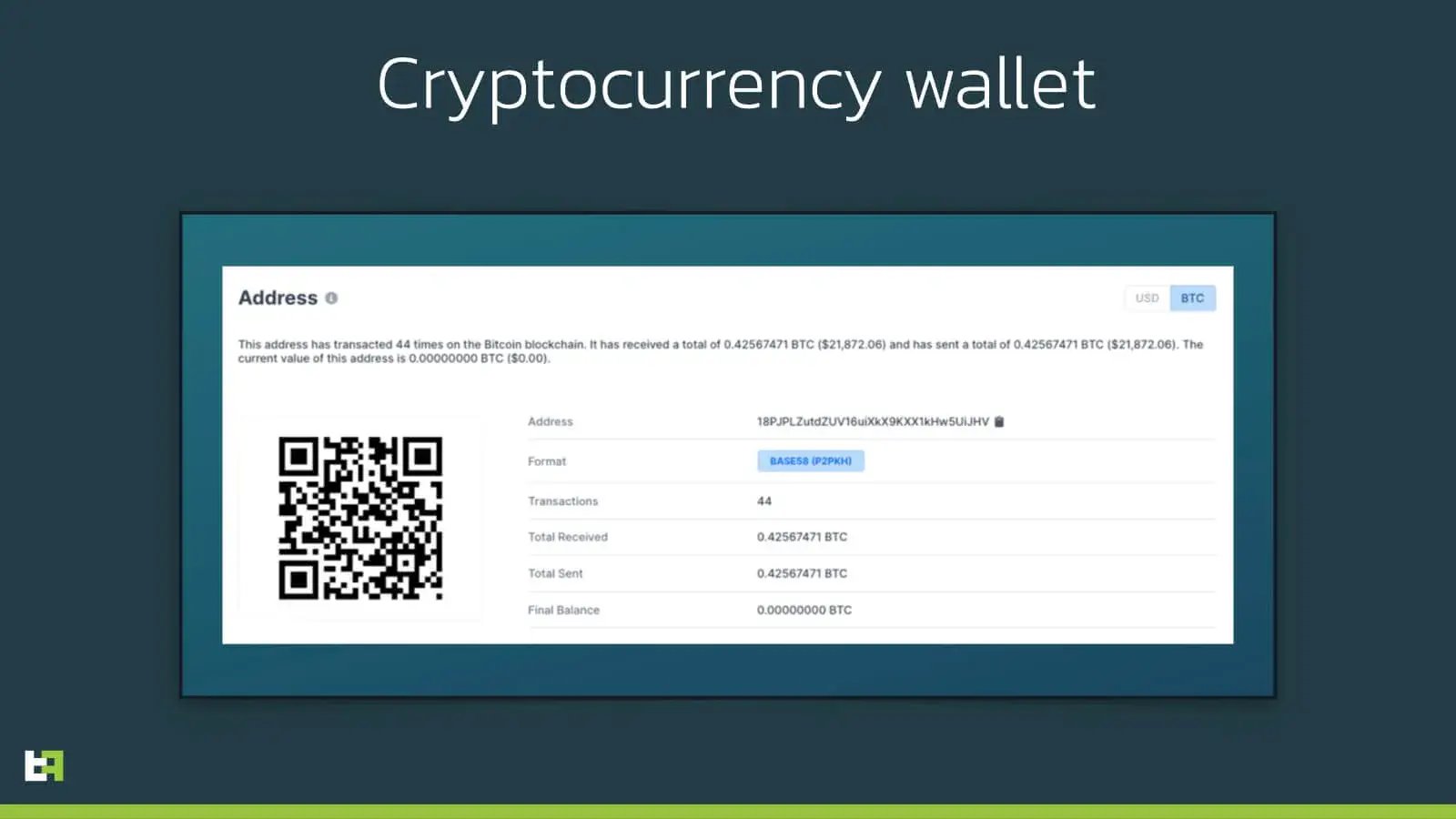
The wallet does have a relative high number of transactions, and a zero balance, indicating that they could be part of a network of wallets used to redirect stolen cryptocurrencies from the victims to the criminals.
C2 Communication
S.O.V.A. relies on the open-source project of RetroFit for its communication with the C2 server.
Retrofit is a type-safe REST client for Android, Java and Kotlin developed by Square. The library provides a powerful framework for authenticating and interacting with APIs and sending network requests with OkHttp.
NOTE : ThreatFabric wants to explicitly mention that RetroFit is a legitimate and legal product. The developers that created this project have no control over the misuse of their software.
C2 methods
Below is a complete list of the methods supported by the bot through its RetroFit client. These are the commands that the bot can send to the C2 to request, or to send back, information. The methods can be sent to API endpoint using a GET message in the form “/api/?method=", plus the parameters required.
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
| bots.update | send ping message |
| push.new | send notification text |
| number.update | send phone number |
| sms.new | send sms text |
| bots.new | registration (gets back the cryptowallet addresses) |
| command.delete | deletes session cookie with c2 |
C2 Endpoints
These are the endpoints reachable on the C2:
| Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|
| /api | Main API endpoint |
| /keylog.php | where Keylog stolen is sent |
| /testpost.php | send keylog and cookie stolen. Used for testing |
| /logpost.php | send logs (v2) |
Updates
As expected with under-development malware, new versions surface very quickly, often adding new features or correcting malfunctions.
S.O.V.A. is no different: in the span of the 24 hours before the planned publishing of this blogpost, the bot passed from version 1 to version 3, adding 3 new commands and some new features. This is already an extensive blog, so we will try to briefly sum up the most important modifications and additions.
New commands
Three new commands were added to S.O.V.A.:
- scancookie (v2)
- stopcookie (v2)
These first two commands add an automation layer to the cookie stealing mechanism. In the first iteration, session stealing could happen only when prompted by a command by the C2. if the command ‘stealer’ was sent, a cookie stealing overlay would be started. With the introduction of this two commands, the criminals can now add applications to a list of “session-stealer targets”, creating a more automatized and scalable option.
- get2fa (v3)
The third command allows criminals to steal 2 Factor Authentication codes from the “Google Authenticator” app, abusing Accessiblility services to launch and log valid codes.
New Features
Two main features were added in the new versions of the malware. These features are the direct effect of open critics suffered by the authors of S.O.V.A. from other malware authors in the forum thread created to sell this bot.
The first feature was added to address the accusation of targeting the CIS region, caused by having some russian institutions in the ‘packageList.txt’ target list. The authors added a country check based on the devices locale and on IP checks, to avoid targeting devices from the following regions:
- Azerbaijan
- Armenia
- Belarus
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Moldova
- Russia
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
Here is a snippet of the corresponding code:
// safe country List: "AZ", "AM", "BY", "KZ", "KG", "MD", "RU", "TJ", "UZ"
private final void checkCountry() {
Timber.d("Running country check", new Object[0]); String v1 = this.getResources().getConfiguration().locale.getCountry(); Intrinsics.checkNotNullExpressionValue(v1, "resources.configuration.locale.country"); if (ConstantsKt.getListCountry().contains(v1)) { Timber.d("Invalid locale. Exit...", new Object[0]);> this.finish(); return; } Function1 v2 = (Function1) new LauncherActivity.checkCountry .1(this); this.retrofitUtil.checkCountry(v2);}in addition, the malware also makes sure to not run whenever the following two Russian banks applications are installed on the device:
| Package | App Name |
|---|---|
| com.idamob.tinkoff.android | Tinkoff |
| ru.sberbankmobile | СберБанк Онлайн |
The second feature correspond to a more extensive support for Chinese phone manufacturers, again following requests from fellow criminals. For these manufactures, the authors added more extensive accesibility service support, to increase the effectiveness of the malware to a wider number of devices.
Future Features
Despite them not being yet advertised or used, the new version also sports some in-the-works code that suggests what new features might be added in the future.
Telegram API support
A new Endpoint API class was added to support Telegram communication. From what we can see, the authors might be inspired by Aberebot, as it looks like this endpoint will be used by the author to monitor any new information gathered by the malware. Here is the definition of the RetroFit Endpoint:
@GET("/bot{botId}/sendMessage")
Object sendInfo(@Path("botId") String arg1,
@Query("chat_id") String arg2,
@Query("parse_mode") String arg3,
@Query("text") String arg4,
Continuation arg5);
There are also another endpoint, called CheckCriptaAPI. This endpoint is not used at the moment, but considering that the author have admitted to have had issues with the ecnryption and obfuscation of their product, this might be a debugging class used for that purpose.
Conclusion
This current year we have observed an explosion of Android banking malware families; in number and volume. The global pandemic has changed the way we interact and resulted in a even sharper increase of mobile payment usage. For this reason, it comes to no surprise that threat actors have followed the massive shift to mobile banking, and are finding ways to exploit newly emerging technologies and changing behaviour.
S.O.V.A. - a new sophisticated malware - is the clear example of this trend. It is still a project in its infancy, and now provides the same basic features as most other modern Android banking malware. However, the author behind this bot clearly has high expectations for his product, and this is demonstrated by the author’s dedication to test S.O.V.A. with third parties, as well as by S.O.V.A.’s explicit feature roadmap.
The current version of S.O.V.A. is capable of stealing credentials and session cookies through overlay attacks, keylogging, hiding notifications, and manipulating the clipboard to insert modified cryptocurrency wallet addresses. If the authors adhere to the roadmap, it will also be able to feature on-device fraud through VNC, DDoS capabilities, Ransomware, and advanced overlay attacks. These features would make S.O.V.A. the most feature-rich Android malware on the market and could become the ‘new norm’ for Android banking trojans targeting financial institutions.
How we help our customers
ThreatFabric makes it easier than it has ever been to run a secure mobile payments business. With the most advanced threat intelligence for mobile banking, financial institutions can build a risk-based mobile security strategy and use this unique knowledge to detect fraud-by-malware on the mobile devices of customers in real-time.
Together with our customers and partners, we are building an easy-to-access information system to tackle the ever growing threat of mobile malware targeting the financial sector. We especially like to thank the Cyber Defence Alliance (CDA) for collaborating and proactively sharing knowledge and information across the financial sector to fight cyber-threats.
ThreatFabric has partnerships with TIPs all over the world.
If you want to request a free trial of our MTI-feed, or want to test our own MTI portal for 30 days, feel free to contact us at: sales@threatfabric.com
If you want more information on how we detect mobile malware on mobile devices, you can directly contact us at: info@threatfabric.com
Appendix
S.O.V.A. Samples
| Obfuscation | Hash |
|---|---|
| Unobfuscated v1 | 8a6889610a18296e812fabd0a4ceb8b75caadc5cec1b39e8173c3e0093fd3a57 |
| Obfuscated v1 | efb92fb17348eb10ba3a93ab004422c30bcf8ae72f302872e9ef3263c47133a7 |
| Obfuscated v2 | dd8a5a1a8632d661f152f435b7afba825e474ec0d03d1c5ef8669fdc2b484165 |
| Obfuscated v3 | b2e592c5cf8ccc944c06a11ff156efdfa4233fe46e2281bab3fd238f03b505e3 |
C2 URL
| URL |
|---|
| hxxp://l8j1nsk3j5h1msal973nk37[.]fun |
| hxxp://a0545193.xsph[.]ru |
Cryptocurrency wallets
During our analysis, we were able to obtain the following cryptocurrency wallet addresses from S.O.V.A.’s C2. After a few days, the C2 stopped sending these as valid responses, and started sending back only placeholder strings.
| Crypto | Address |
|---|---|
| BTC | 18PJPLZutdZUV16uiXkX9KXX1kHw5UiJHV |
| ETH | 0xbD1bB3101fCc1A2724C3c5c4F10Fa062DF87E134 |
| BNB | bnb1lwf4kzw74wuf0zmsg25fjh44pzpdwhavn3n9dq |
| TRX | TUGyDe7eGJi2DVDMxc2KExksF29vHsZcQm |
Targets
This is a list of the institutions or applications that are targeted via overlay:
| Institution / Application |
|---|
| mail.com |
| Deutsche Bank |
| Netflix |
| BBVA Net Cash ES & PT |
| Caixa Geral de Depósitos |
| Bankia |
| Cajalnet |
| Bi en Línea |
| UnicajaMovil |
| Bankinter Móvil |
| Santander Empresas |
| Pibank |
| Ibercaja |
| ABANCA Empresas |
| Banca Móvil Laboral Kutxa |
| Kutxabank |
| NBapp Spain |
| BBVA Spain |
| imaginBank - Your mobile bank |
| Cajasur |
| Santander |
| Goole Passwords |
| Gmail |
| password |
| yahoo mail |
| AT&T |
| Verizon |
| Blockhchain |
| Trust Wallet |
| Coinbase |
| BBVA |
| Suntrust |
| PNC Bank |
| Bank of America |
| Capital ONE |
| Citi Bank |
| Citizen |
| SunCorp |
| USAA Bank |
| Wells Fargo |
| PayPal |
| Uber |
| EVO banco |
In case any of the following packages is present in the victim’s device, the criminals are notified:
| PackageName | AppName |
|---|---|
| com.google.Android.apps.authenticator2 | Google Authenticator |
| com.bankaustria.Android.olb | Bank Austria MobileBanking |
| com.cibc.Android.mobi | CIBC Mobile Banking® |
| com.rbc.mobile.Android | RBC Mobile |
| cz.airbank.Android | My Air |
| com.kutxabank.Android | Kutxabank |
| es.lacaixa.mobile.Android.newwapicon | CaixaBank |
| com.mtel.Androidbea | BEA 東亞銀行 |
| jp.co.aeonbank.Android.passbook | イオン銀行通帳アプリ かんたんログイン&残高・明細の確認 |
| com.barclays.ke.mobile.Android.ui | Barclays Kenya |
| nz.co.anz.Android.mobilebanking | ANZ goMoney New Zealand |
| alior.bankingapp.Android | Usługi Bankowe |
| wit.Android.bcpBankingApp.millenniumPL | Bank Millennium |
| com.idamobile.Android.hcb | Мобильный банк - Хоум Кредит |
| ru.rosbank.Android | ROSBANK Online |
| com.vkontakte.Android | VK — live chatting & free calls |
| ru.taxovichkof.Android | Taxovichkof |
| hr.asseco.Android.jimba.mUCI.ro | Mobile Banking |
| may.maybank.Android | Maybank2u |
| com.amazon.mShop.Android.shopping | Amazon Shopping - Search, Find, Ship, and Save |
| ru.alfabank.mobile.Android | Альфа-Банк (Alfa-Bank) |
| com.idamob.tinkoff.Android | Tinkoff |
| ru.vtb24.mobilebanking.Android | VTB-Online |
| com.akbank.Android.apps.akbank_direkt | Akbank |
| com.akbank.Android.apps.akbank_direkt_tablet | Akbank Direkt Tablet |
| com.akbank.Android.apps.akbank_direkt_tablet_20 | - |
| com.ykb.Android | Yapı Kredi Mobile |
| com.ykb.Android.mobilonay Y | apı Kredi Corporate-For Firms |
| com.ykb.Androidtablet | Yapı Kredi Mobil Şube |
| biz.mobinex.Android.apps.cep_sifrematik | Garanti BBVA Cep Şifrematik |
| com.matriksmobile.Android.ziraatTrader | Ziraat Trader |
| de.comdirect.Android | comdirect mobile App |
| de.fiducia.smartphone.Android.banking.vr | VR Banking Classic |
| fr.creditagricole.Androidapp | Ma Banque |
| com.boursorama.Android.clients | Boursorama Banque |
| com.caisseepargne.Android.mobilebanking | Banque |
| fr.lcl.Android.customerarea | Mes Comptes - LCL |
| com.paypal.Android.p2pmobile | PayPal Mobile Cash: Send and Request Money Fast |
| com.usaa.mobile.Android.usaa | USAA Mobile |
| com.chase.sig.Android | Chase Mobile |
| com.grppl.Android.shell.BOS | Bank of Scotland Mobile Banking: secure on the go |
| com.rbs.mobile.Android.natwestoffshore | NatWest International |
| com.rbs.mobile.Android.natwest | NatWest Mobile Banking |
| com.rbs.mobile.Android.natwestbandc | NatWest Business Banking |
| com.rbs.mobile.Android.rbs | Royal Bank of Scotland Mobile Banking |
| com.rbs.mobile.Android.rbsbandc | RBS Business Banking |
| com.rbs.mobile.Android.ubr | Ulster Bank RI Mobile Banking |
| com.grppl.Android.shell.halifax | Halifax: the banking app that gives you extra |
| com.grppl.Android.shell.CMBlloydsTSB73 | Lloyds Bank Mobile Banking: by your side |
| com.barclays.Android.barclaysmobilebanking | Barclays |
| com.unionbank.ecommerce.mobile.Android | Union Bank Mobile Banking |
| au.com.ingdirect.Android | ING Australia Banking |
| com.cba.Android.netbank | CommBank app for tablet |
| com.anz.Android.gomoney | ANZ Australia |
| com.anz.Android | ANZ Mobile Taiwan |
| de.fiducia.smartphone.Android.banking.vr | VR Banking Classic |
| it.volksbank.Android | Volksbank · Banca Popolare |
| de.fiducia.smartphone.Android.securego.vr | VR-SecureGo |
| com.starfinanz.smob.Android.sfinanzstatus | Sparkasse Ihre mobile Filiale |
| com.starfinanz.mobile.Android.pushtan | S-pushTAN |
| com.starfinanz.smob.Android.sfinanzstatus.tablet | Sparkasse fürs Tablet |
| com.starfinanz.smob.Android.sbanking | Sparkasse+ Finanzen im Griff |
| com.palatine.Android.mobilebanking.prod | ePalatine Particuliers |
| es.cm.Android | Bankia |
| es.cm.Android.tablet | Bankia Tablet |
| com.bestbuy.Android | Best Buy |
| com.latuabancaperAndroid | Intesa Sanpaolo Mobile |
| com.latuabanca_tabperAndroid | La tua banca per Tablet |
| it.copergmps.rt.pf.Android.sp.bmps | Banca MPS |
| com.ykb.Android | Yapı Kredi Mobile |
| aib.ibank.Android | AIB Mobile |
| com.jpm.sig.Android | J.P. Morgan Mobile |
| pinacleMobileiPhoneApp.Android | PINACLE® |
| com.fuib.Android.spot.online | PUMB Online |
| com.ukrsibbank.client.Android | UKRSIB online |
| ru.alfabank.mobile.ua.Android | Alfa-Mobile Ukraine |
| ua.aval.dbo.client.Android | Raiffeisen Online Ukraine |
| ua.com.cs.ifobs.mobile.Android.otp | OTP Smart |
| ua.com.cs.ifobs.mobile.Android.pivd | Pivdenny MyBank |
| io.getdelta.Android | Delta - Bitcoin & Cryptocurrency Portfolio Tracker |
| com.coinbase.Android | Coinbase – Buy & Sell Bitcoin. Crypto Wallet |
| piuk.blockchain.Android | Blockchain Wallet. Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum |
| com.thunkable.Android.santoshmehta364.UNOCOIN_LIVE | UNOCOIN LIVE |
| com.thunkable.Android.manirana54.LocalBitCoins | LocalBitCoins |
| com.thunkable.Android.manirana54.LocalBitCoins_unblock | UNBLOCK Local BitCoins |
| com.citizensbank.Androidapp | Citizens Bank Mobile Banking |
| com.navyfederal.Android | Navy Federal Credit Union |