Xenomorph Malware Strikes Again: Over 30+ US Banks Now Targeted
25 September 2023

Jump to
A New Xenomorph Campaign
Anyone familiar with the famous movie "Alien", directed by Ridley Scott in 1979, is well aware of how hard it is to get rid of the titular monsters of this franchise. Despite all the efforts from the protagonists, the monsters seem to always return.
When we discovered and named Xenomorph, in February 2022, we would never have been able to predict how similar this malware family could be to its cinematic counterpart.
Back in August 2023 ThreatFabric’s cyber fraud analysts once again came across some new samples of Xenomorph.
From what was observed in previous cases, we were able to clearly identify a distribution campaign, using phishing webpages to trick victims into installing malicious APKs, which feature a larger list of targets compared to its previous versions.
This new list adds dozens of new overlays for institutions from the United States, Portugal, and multiple crypto wallets, following a trend that has been consistent amongst all banking malware families in the last year.
ThreatFabric was also able to analyse an ongoing campaign, with thousands of downloads of Xenomorph in Spain and the United States.
This is not unusual as many other malware families have started expanding their area of interest across the Atlantic Ocean, including the most distributed MaaS (Malware-as-a-Service) families, such as Octo, Hydra, and Hook, and some of the most notorious privately operated families, such as Anatsa.
As a consequence to the Device Take-Over capabilities offered by these families, it is now easier than ever for criminals to move across different markets and perform fraud with little or no infrastructure required.
In this article, we will cover our latest research on Xenomorph, starting from a technical point of view, as well as address the distribution framework used by the Threat Actors behind this campaign, and its connections to other malware families, as well as Windows Desktop malware distributed side-by-side with it.
Xenomorph is Back Once Again
Xenomorph is a very advanced malware family, which runs the gamut from simple SMS manipulation to full device control, due to a very powerful Automated Transfer System (ATS) framework obtained via Remote Access capabilities offered by accessibility services privileges. This malware family has been in constant evolution since its discovery in early 2022, adding continuous features over the months.
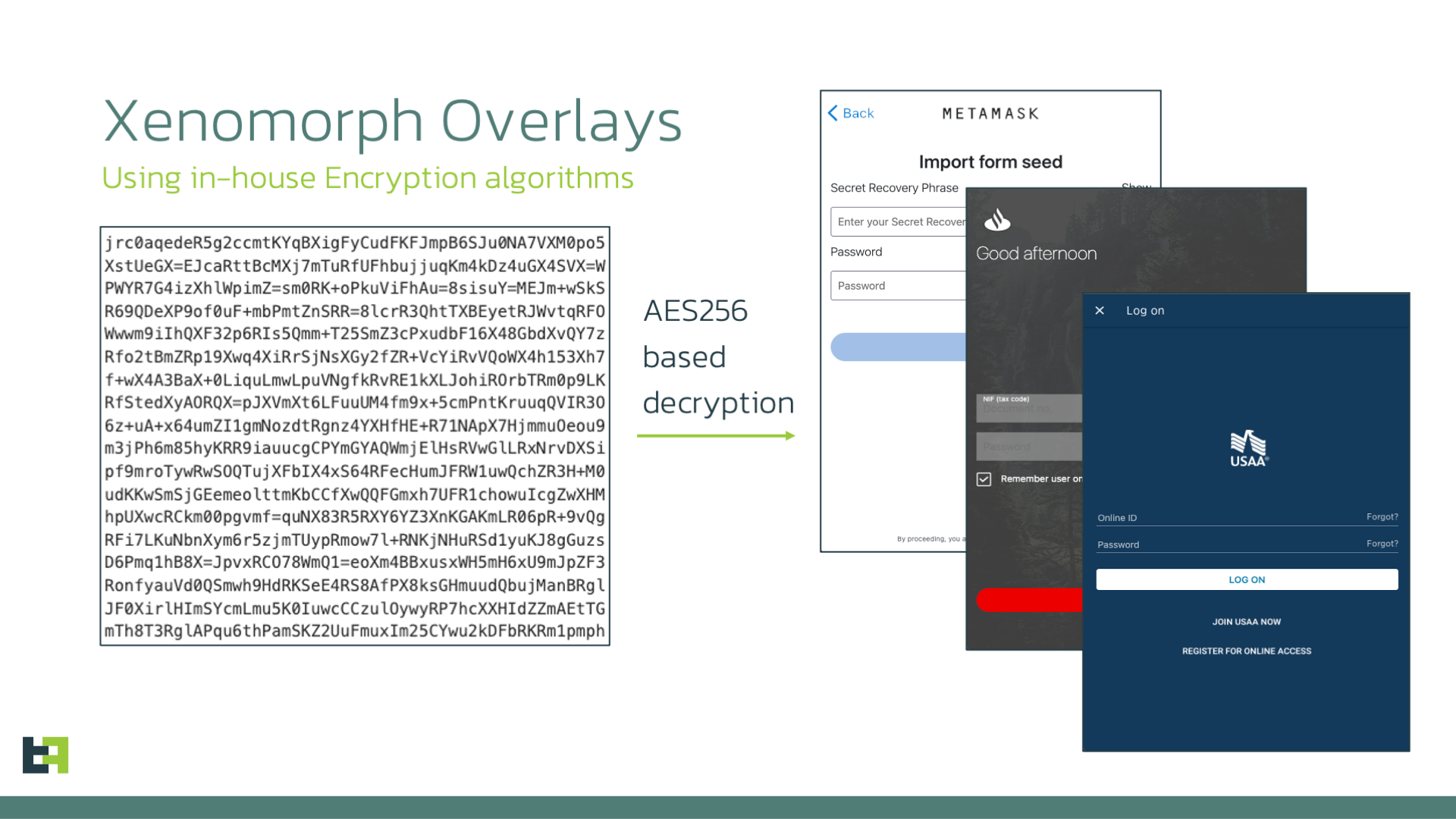
Xenomorph uses overlays as its main way to obtain Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, and much more. The control server transmits to the bot a list of URLs containing the address from which the malware can retrieve the overlays for the infected device.
Such overlays are encrypted using a combination of an algorithm specific to Xenomorph and AES. Once decrypted, the overlay poses as login pages for the targeted applications:
Its main feature is the very flexible ATS Engine, which offers a vast quantity of actions that can be used and chained into sequences of operations, triggered when specific conditions are met. Threat Actors refer to these sets of actions as "modules" of their engine. The malware contains in its configuration a large set of modules, which mostly offer possibilities to manipulate the infected device's settings, for example by granting write permission to the malware or disabling Doze mode (a mode that conserves battery by restricting apps' access to network and CPU-intensive services).
The list of modules available in the malware's hardcoded and encrypted configuration is very similar to the previous variant of Xenomorph that we reported earlier this year. In this version, a new module was added, which is highlighted in bold in the table below:
| Module name | description | |
|
notificationAccess
|
Grant notification access
|
|
|
grantPermissions
|
Automatically grants itself all permissions required
|
|
|
dozeModeDisableTypeA
|
Disable Doze mode (Xiaomi MIUI) - version 1
|
|
|
dozeModeDisableTypeB
|
Disable Doze mode (Xiaomi MIUI) - version 2
|
|
|
dozeModeDisableTypeC
|
Disable Doze mode (Xiaomi MIUI) - version 3
|
|
|
dozeModeDisableTypeD
|
Disable Doze mode (Xiaomi MIUI) - version 4
|
|
|
disablePlayProtect
|
Disable Play Protect
|
|
|
xiaomiAdminAccess
|
Get Admin Access Xiaomi
|
|
|
restrictUninstall_SamsungApi29
|
Stop uninstall procedure in Samsung using API 29 (Android 10)
|
|
|
dismissSettingsAlerts_Generic
|
Dismiss Settings Alerts
|
|
|
restrictReset_Generic
|
Stop device reset
|
|
|
restrictReset_ByContentVid_SamsungApi30
|
Stop device reset in Samsung using API 30 (Android 11)
|
|
|
restrictUninstall_ByClassName
|
Stop uninstall procedure based on Class name
|
|
|
restrictUninstall_Generic
|
Stop uninstall procedure
|
|
|
restrictAccessibilityDisable_Generic
|
Stop disabling of Accessibility Services privileges
|
|
|
restrictAdminRetrieve_XiaomiApi30
|
Restrict retrieving Admin in Xiaomi using API 30 (Android 11)
|
|
|
restrictSettingsClicks_Generic
|
Restrict clicks in settings
|
|
|
defaultSmsApp-Alert
|
Interface with Default SMS settings Alert
|
|
|
defaultSmsApp-Role-ChangePrevention
|
Prevent removal of Default SMS Role
|
|
|
defaultSmsApp-Role
|
Obtain Default SMS role
|
|
|
defaultSmsApp-Settings
|
Set as Default SMS Handler
|
|
|
grantWriteStoragePermissions
|
Grants write storage permissions
|
|
|
grantSystemWritePermissions
|
Grants system write permissions
|
|
|
getGoogle2FA
|
Gets Google Authenticator 2FA codes
|
The list includes multiple modules dedicated to precise actions for specific Mobile User Interfaces based on AOSP (Android Open Source Project), for example MIUI in the case of Xiaomi or One UI in the case of Samsung. This is necessary because different UIs require a unique order of operations to perform specific actions, like disabling Doze mode.
Actors have put a lot of effort into modules that support Samsung and Xiaomi devices. This makes sense, considering that these two combined make up roughly 50% of the whole Android market share, according to recent data presented in multiple recent studies.
These modules are built in the same way we discussed in our previous blog, but we will report here the structure for convenience. Each module is saved in JSON format, with multiple entries, structured in the following way:
{"module": "<MODULE_NAME>","version": 1,"parameters": [...], // LIST OF PARAMETERS"requires": [...], // LIST OF REQUIRED CONDITIONS"triggerConditions": [...], // LIST OF TRIGGER CONDITIONS"terminator": {...}, // IS TERMINATOR ENABLED"operations": [...] // LIST OF OPERATIONS TO BE EXECUTED (ATS)}
This system gives criminals the building blocks required to recreate the flow of a decision algorithm. This means that the ATS modules are not simply a list of actions to execute one after the other: with the to the "triggerConditions", "requires", and "terminator" parameters, the ATS engine is capable of performing conditional checks and loops, vastly increasing its flexibility.
The full list of operations that can be used in this engine is quite extensive but has not been modified from Xenomorph's previous version. If you are interested in this list, which includes actions to press specific buttons, perform global actions (Home screen, Back, etc.), and search for specific text in the UI, you can refer to our previous article regarding this malware family.
New Capabilities
From a purely technical point of view, this new campaign of Xenomorph does not feature major modifications from its previous iteration. This is a testament to the maturity of this Android Banker. Most of the work from the Threat Actors operating Xenomorph is going into developing additional ATS modules, and most importantly distributing their product.
This does not mean that the malware is completely identical to its predecessor.
Here is a list of new commands added by Xenomorph (the full list is available in the Appendix of this article):
| Command | Description |
|
start_mimic
|
Start Mimic Function |
|
stop_mimic
|
Stop Mimic Function |
|
show_push (antisleep feature)
|
Enable antisleep push notification
|
|
clickOnPoint
|
simulate a touch on specific coordinates
|
Antisleep Feature
This feature allows criminals to set a flag in the shared preferences file, which tells the malware that the device should not go into sleep mode (i.e., the screen should never turn off).
Whenever the flag "antisleep" is set, the malware maintains an active notification, which keeps the device awake, preventing it from going to sleep.
The code is contained in the logic of the command "show_push", responsible for displaying push notifications.
If the "antisleep" tag exists and is set to true, then the malware will create a default push notification. If it is set to false it will clear it, allowing the device to go back to sleep.
If the malware wants to push a customised notification, then it will delete the flag altogether and will receive from the C2 the parameters required to create such a notification.
'Mimic' Feature
Threat Actors have also added a new feature, referred to as "mimic" in the code.
This feature is enabled or disabled using the "start_mimic" and "stop_mimic".
Effectively, whenever the malware is launched, it checks if this mimic mode is active. If it is, it will automatically launch another activity that was communicated as a parameter with the start_mimic command. This gives the option to the malware to act as any other application, and more importantly, removes one behaviour that is often associated with malware. The code contains an activity called IDLEActivity, which is used as a webView to display a legitimate website.
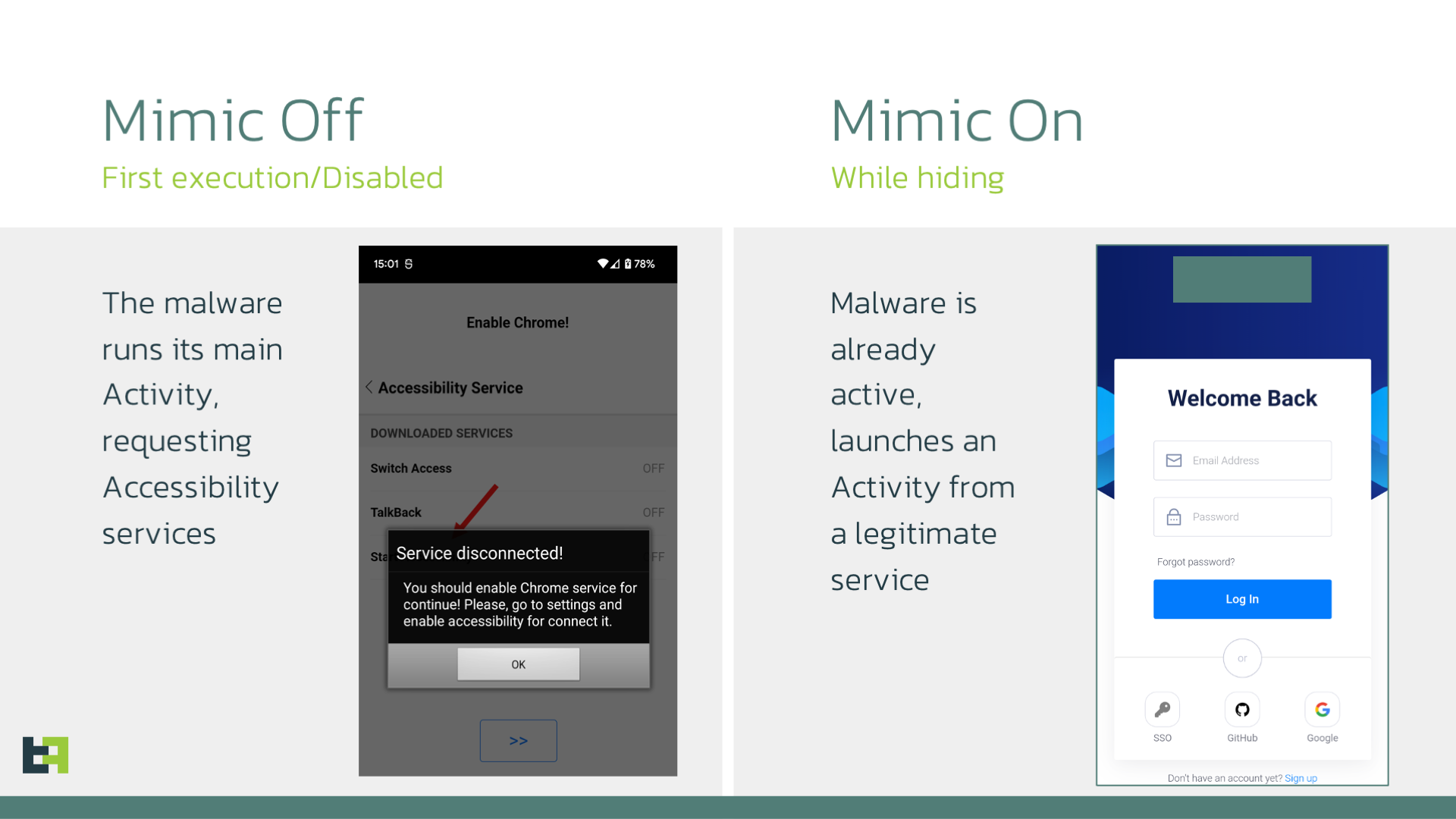
In most cases, after the first execution, malware hides its icon from the launcher, in order to pass unnoticed for the longest time possible. However, this is also something that can be checked by security products, and it increases the risk score associated with a specific application.
By posing as another application, Xenomorph can avoid using this technique, avoiding triggering one of the many behaviours typical of Android malware.
In the samples observed the code for this feature is available, but it is manually disabled with a hardcoded flag. We expect this to change in the near future.
ClickOnPoint Feature
Finally, the last command added by the authors or Xenomorph is the ability to simulate a simple touch at specified coordinates, using the "clickOnPoint" command.
This is not an incredibly advanced feature, and definitely not the most complex that Xenomorph offers, however, it allows criminals to perform small actions without having to create a full ATS module.
This command adds more flexibility to the whole process:
if (!apiCommand0.command.equals("clickOnPoint") ||
apiCommand0.parameters == null ||
((String)apiCommand0.parameters.get("x")) == null ||
((String)apiCommand0.parameters.get("y")) == null) {
continue;
}
Integer integer0 = Integer.parseInt(((String)apiCommand0.parameters.get("x")));
Integer integer1 = Integer.parseInt(((String)apiCommand0.parameters.get("y")));
UtilAccessibility.click(App.getAccessibilityService(), integer0.intValue(), integer1.intValue());
Target Analysis
Overlays
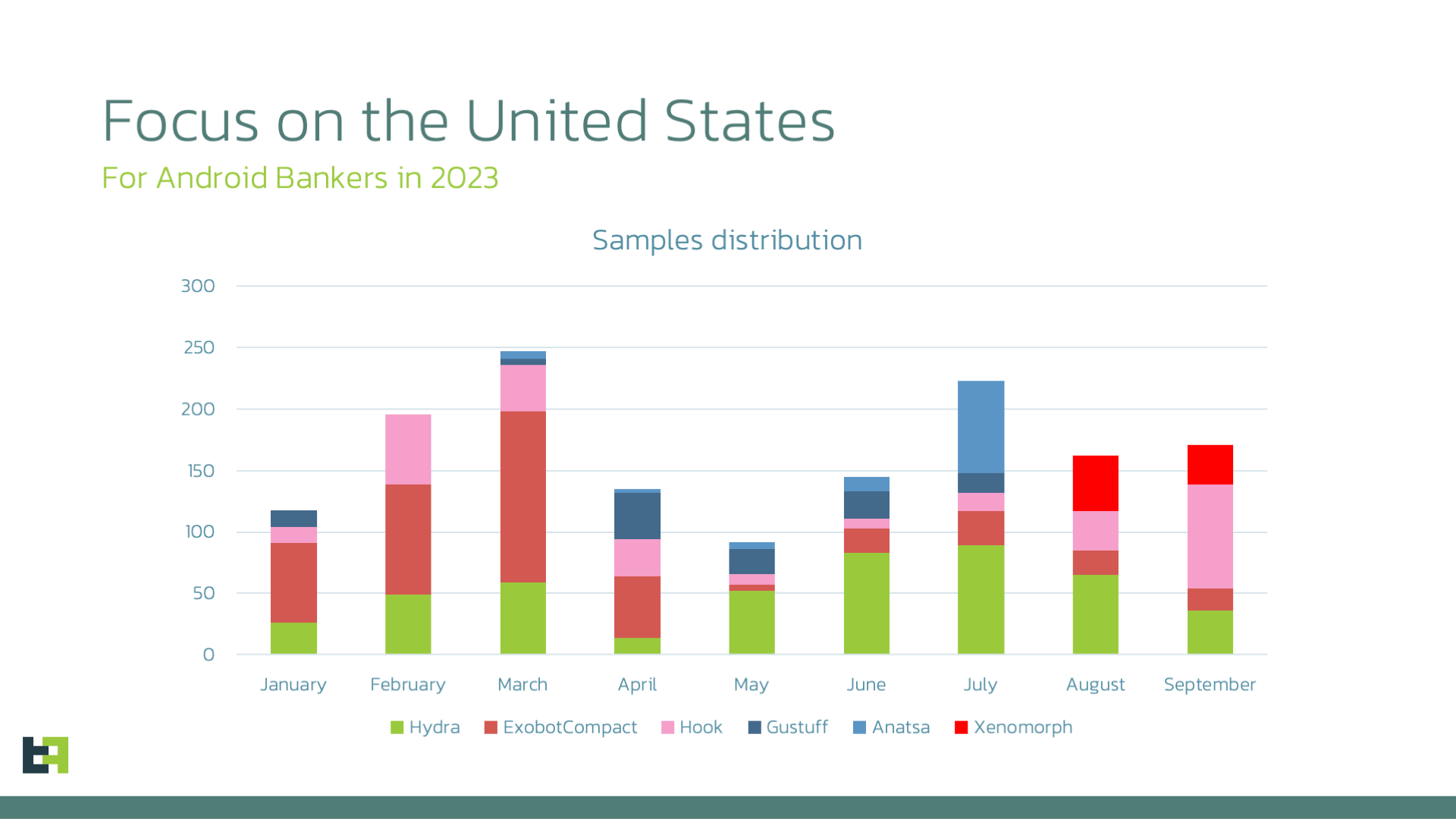
The most recent samples of this new Xenomorph campaign date back to mid-August 2023, and were identified by the appTag "RUN-AUG1508-HIDE-1". This tag, apart from helping us identify the period of activity connected with this specific campaign, also indicates the likelihood of a recurrence of such activity.
We were able to identify a few dozen samples belonging to this campaign, connected with a targeted effort in the same areas we identified in what we defined as a "live campaign" in our previous article.
These areas include Spain, Portugal, Italy, Canada, and Belgium.
However, this latest campaign also added plenty of financial institutions from the United States, together with multiple crypto-wallet applications, totaling more than 100 different targets per sample, each one using a specifically crafted overlay to steal precious PII from the victim's infected device.
As mentioned in the introduction, this is a trend that we consistently observe in all modern malware families.
With the ubiquity of mobile banking adoption from institutions from all over the world, it is only logical that criminals are taking this opportunity to expand their activity to previously untapped markets.
Distribution
ThreatFabric was able to identify active campaigns distributing the malware via phishing pages. In these cases, the malware was distributed through phishing pages posing as a Chrome update.
This is in line with the standard lures used by many other malware families: usually with applications that are very common and generic, like Google Chrome browser or Google Play store, raise fewer suspicions among victims, who are extremely likely to have them already installed on their device.
In this specific case, however, actors made the vital mistake of not restricting access to the server folder containing the files necessary to distribute the malware (not a first when it comes to Xenomorph).
This allowed us to monitor the server, identifying multiple interesting files.
One of them is named count.txt, and contains a list of entries, made up of IPs, user agents, and dates. Upon further investigation, we were able to confirm that these were the IPs of devices downloading the payload of the phishing page.
This gave us very valuable information about the actual downloads of this Xenomorph campaign.
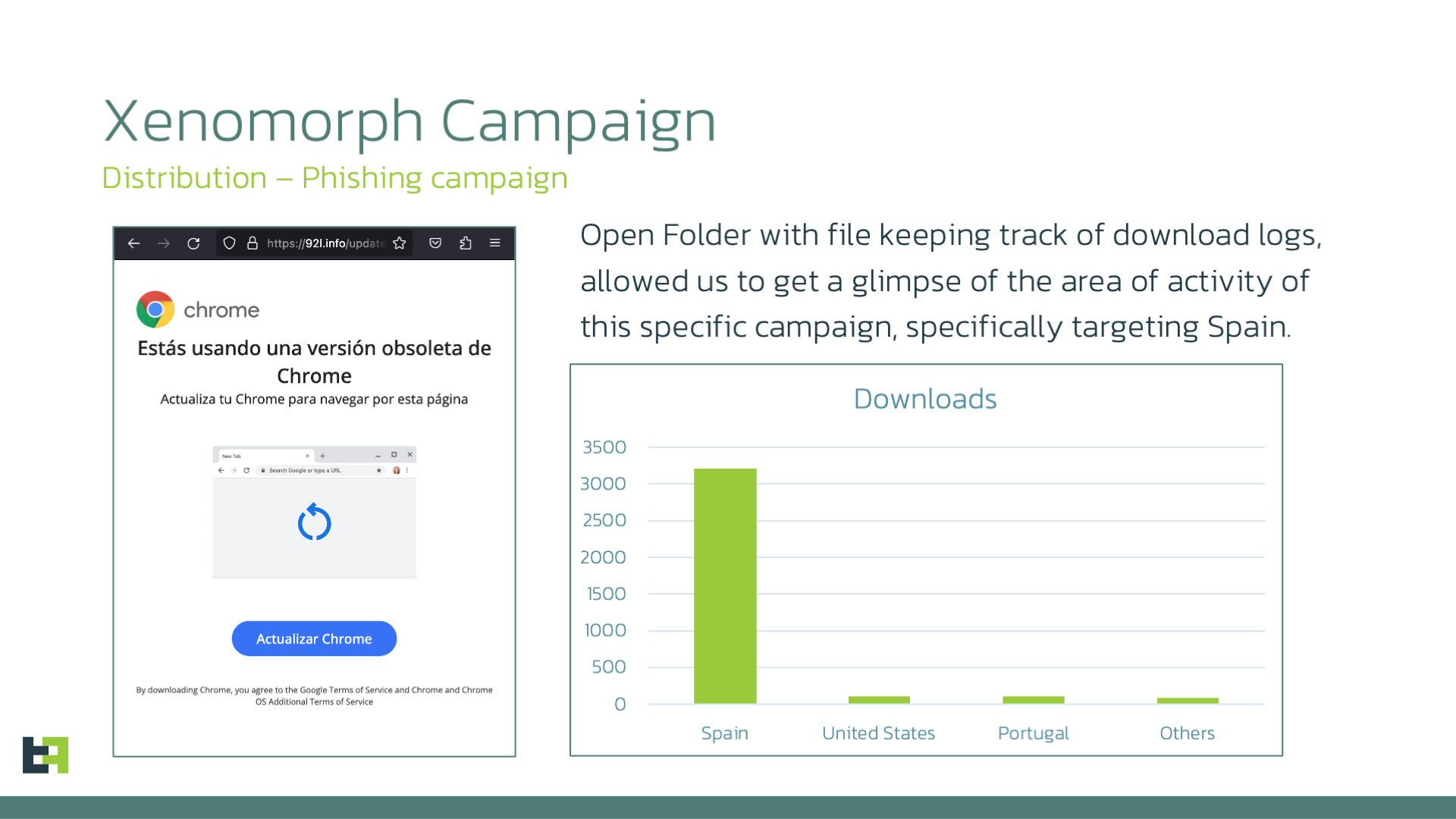
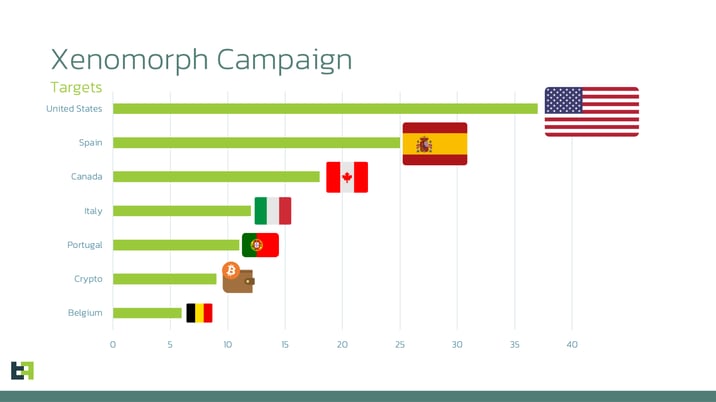
From the graph, it is clear that this campaign is heavily focused on Spain, with more than 3,000 downloads in the span of a few weeks, followed by a large margin of downloads from the United States and Portugal, with more than 100 downloads each.
It is worth noting that, a few days before the publishing of this article, the drop point change payload, started distributing ExobotCompact/Octo.
The reason behind this event could be one of the following:
- The server is used by one actor, using multiple threats, testing each one.
- The server is part of a distribution service, where the samples to be distributed are handed over to distributor which places them on one server for different campaigns of different operators.
Both cases are possible, and we have actually reported instances of each in the past. The first case is still connected to Xenomorph, being distributed side-by-side with Ermac payloads using Zombinder droppers.
The second case dates back to 2022, with the same infrastructure distributing both Medusa and Cabassous.
Currently, we do not have conslusive evidence to prove either of these hypothesis, but we will continue to monitor the infrastructure to gain more information.
Desktops are also Targeted
However, other files also caught our analysts' attention: further analysis of the files revealed that they are related to several quite well-known Desktop stealers: malware designed to steal credentials from victims’ machines.
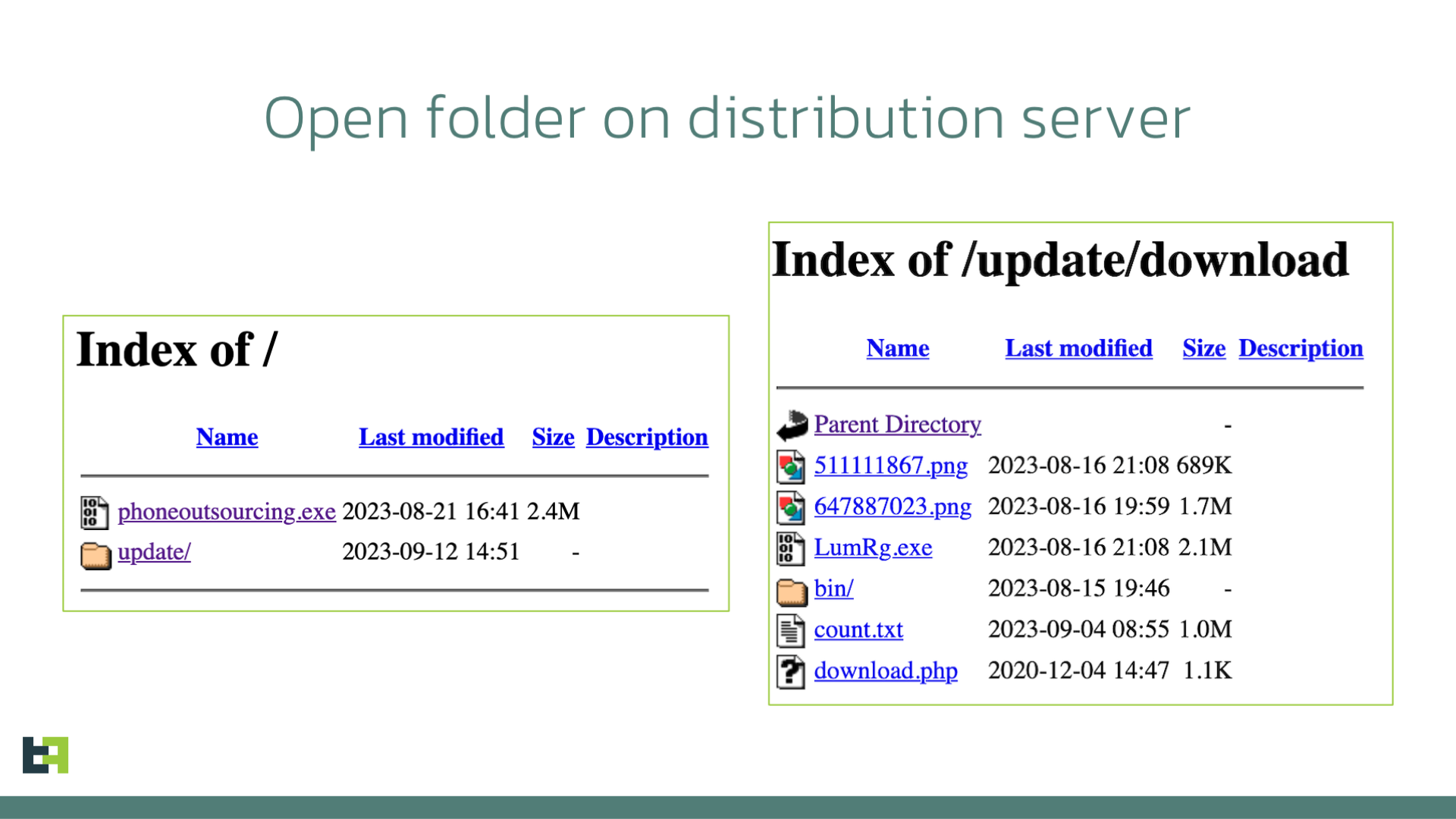
In the following sections we cover two interesting files: "phoneoutsourcing.exe" related to RisePro stealer and "647887023.png" being one of the stages leading to infection with LummaC2 stealer.
Stealer on the Rise: RisePro stealer with Private Loader traces
RisePro stealer is a well-known credential stealer within the desktop malware threat landscape. It is also known to have certain connections to other prominent malware families: Private Loader, as reported by Sekoia.io. is another example of Malware-as-a-Service advertised on underground forums.
First discovered in December 2022, RisePro remained quiet for some time, coming back again in July 2023. This time several advertisements were placed in underground forums promoting the renewed service.

The capabilities of the stealer are rather wide, including:
- Stealing of credentials, credit cards, and cookies from a wide range of browsers and browser extensions;
- Credentials from software, including cryptocurrency wallets and e-mail clients;
- File grabbing by name pattern;
- Arbitrary file downloading.
Monitoring of RisePro developer accounts showed that the malware receives constant updates and enhancements. The analysis of the file discovered on the distribution website showed that it is indeed RisePro stealer, with traces leading to another popular malware family Private Loader.
However, a previously undocumented change was discovered in this malware: the communication protocol with C2 was updated and instead of HTTP it uses raw TCP sockets over port 50500 to receive commands and exfiltrate data.
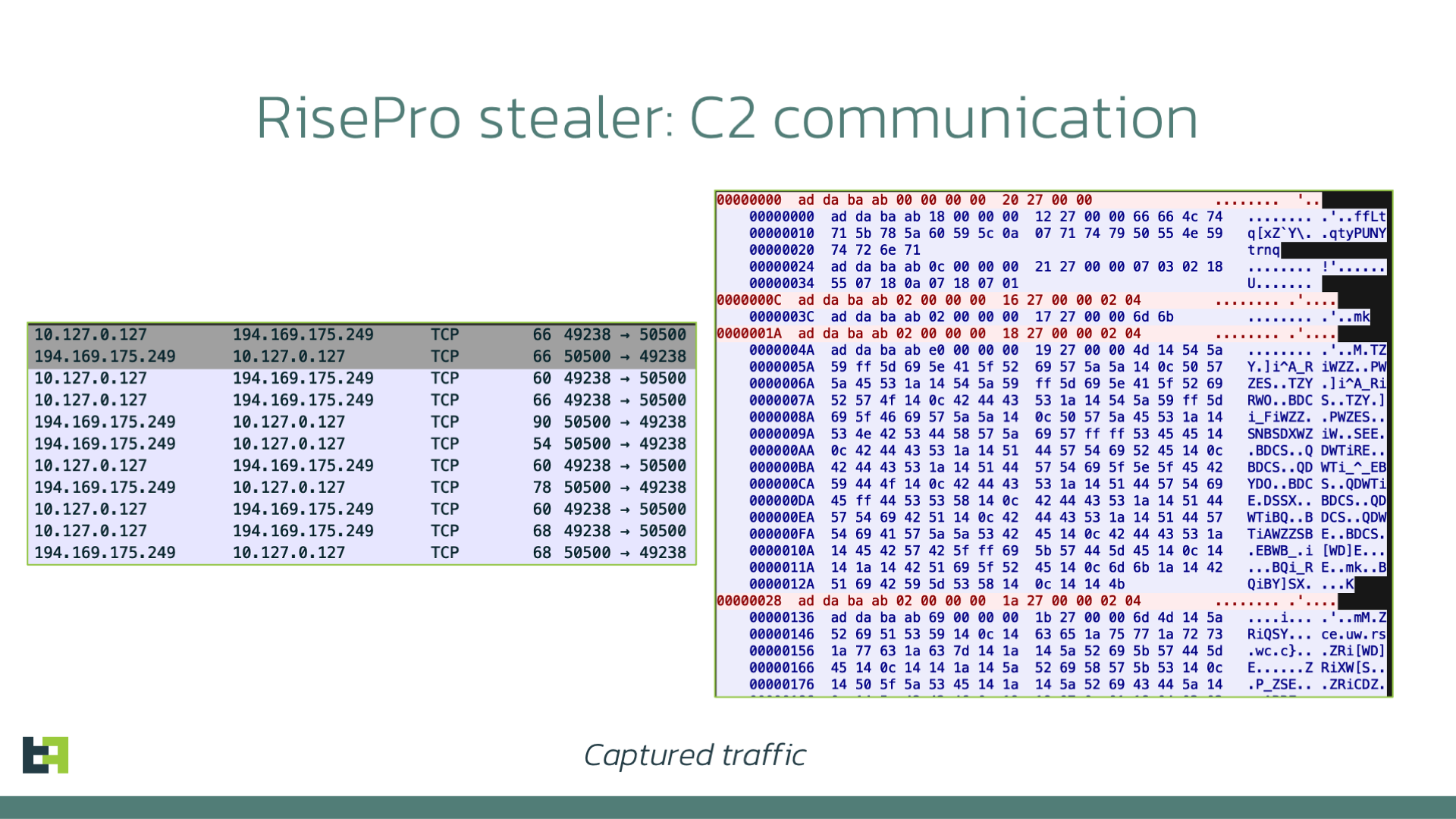
The structure of the packet is as follows:
- Header “\xad\xda\xba\xab” (DWORD)
- Size of the encrypted data (DWORD)
- Packet/command ID (DWORD)
- Encrypted data
The data is encrypted with the same substitution table and XOR key as described in the Sekoia.io blog, after decryption the JSON structure with configurations is retrieved:

The analysis of the C2 reveals the login panel of RisePro stealer, once again proving the relation:

LummaC2 is also here
The nature of the files found on the distribution server shows that it is very likely a part of a distribution service that might be used by multiple actors. However, there is also a possibility that all these files belong to one actor who is trying several Malware-as-a-Service “providers” to test them and see the outcome, focusing not only on mobile devices but also desktops, trying to reach a wider audience and grab as many credentials as possible.
Further analysis of the host on VirusTotal revealed a connection to ZIP archive called “BrowserUpdate.zip” (similar to masquerading by Xenomorph and Octo) which was seen contacting the server and downloading one of the “PNG” files. Further examination of the files revealed its connection to another well-known stealer, LummaC2.

Its functionality is not significantly different from other stealers, aiming to steal huge amounts of credentials and sensitive data from victims’ machines.
There is such a variety of malicious tools found on one server that we can conclude with much confidence that actors behind it test different Malware-as-a-Service to find out the most profitable ones.
Conclusion
This investigation once again highlights the continuous efforts of criminals to perfect their products and expand their reach, in order to maximize their profits.
Xenomorph, after months of hiatus, is back, and this time with distribution campaigns targeting some regions that have been historically of interest for this family, like Spain or Canada, and adding a large list of targets from the United States, as well as multiple new Cryptowallets.
ThreatFabric was able to analyse one specific campaign, connecting it with thousands of downloads predominantly from Spain, followed by the United States and other European major countries.
Xenomorph maintains its status as an extremely dangerous Android Banking malware, featuring a very versatile and powerful ATS engine, with multiple modules already created, with the idea of supporting multiple manufacturer's devices.
The fact that we saw Xenomorph being distributed side-by-side with powerful desktop stealers is very interesting news. It could indicate a connection between the threat actors behind each of these malware, or it could mean that Xenomorph is being officially sold as a MaaS to actors, who operate it together with other malware families. In each case, it indicates an activity from Xenomorph which we have not seen before, but which we might see a lot of in the near future.
Fraud Risk Suite
ThreatFabric’s Fraud Risk Suite enables safe & frictionless online customer journeys by integrating industry-leading mobile threat intel, behavioral analytics, advanced device fingerprinting, and over 10,000 adaptive fraud indicators. This will give you and your customers peace of mind in an age of ever-changing fraud.
Appendix
Xenomorph Samples
| Hash (sha256) | App name | package name |
| e2646afca109162f66b117ca8a7feed0272ab6d8822132dafd2d54d7553cbfde | Chrome | com.peace.frequent |
| 259e88f593a3df5cf14924eec084d904877953c4a78ed4a2bc9660a2eaabb20b | Chrome | com.mtnyrvojt.qtbxtwjnq |
| 257f041d1b6ed82808cd8ef07ec84cf141c38e5374b654de46879a3bc180c79c | Chrome | com.uhtvqsutg.igogiciut |
Xenomorph C2 servers
| Server url/ip | Role |
| airlinesimulator[.]io | Overlay Server |
| fobocontentplus[.]online | C2 Server |
| fobocontentplus[.]top | C2 Server |
| fobocontentplus[.]site | C2 Server |
| 92l[.]info | Phishing Server |
Xenomorph Targets
Highlighted in bold are the newly added targets:
| package name | app name | country |
|
com.ally.MobileBanking |
Ally Mobile |
United States |
|
com.americanexpress.android.acctsvcs.us |
Amex |
United States |
|
com.aol.mobile.aolapp |
AOL - News, Mail & Video |
United States |
|
com.att.myWireless |
myAT&T |
United States |
|
com.bancorpsouth.android |
BancorpSouth Mobile |
United States |
|
com.bbt.myfi |
U by BB&T |
United States |
|
com.botw.mobilebanking |
Bank of the West Mobile |
United States |
|
com.chase.sig.android |
Chase Mobile |
United States |
|
com.citi.citimobile |
Citi Mobile® |
United States |
|
com.citizensbank.androidapp |
Citizens Bank Mobile Banking |
United States |
|
com.compasssavingsbank.mobile |
Compass Savings Bank |
United States |
|
com.discoverfinancial.mobile |
Discover Mobile |
United States |
|
com.etrade.mobilepro.activity |
E*TRADE: Invest. Trade. Save. |
United States |
|
com.huntington.m |
Huntington Mobile |
United States |
|
com.infonow.bofa |
Bank of America Mobile Banking |
United States |
|
com.konylabs.capitalone |
Capital One® Mobile |
United States |
|
com.mcom.firstcitizens |
First Citizens Mobile Banking |
United States |
|
com.mfoundry.mb.android.mb_136 |
People's United Bank Mobile |
United States |
|
com.morganstanley.clientmobile.prod |
Morgan Stanley Wealth Mgmt |
United States |
|
com.mtb.mbanking.sc.retail.prod |
M&T Mobile Banking |
United States |
|
com.navyfederal.android |
Navy Federal Credit Union |
United States |
|
com.pnc.ecommerce.mobile |
PNC Mobile |
United States |
|
com.schwab.mobile |
Schwab Mobile |
United States |
|
com.sovereign.santander |
Santander Bank US |
United States |
|
com.suntrust.mobilebanking |
SunTrust Mobile App |
United States |
|
com.tdbank |
TD Bank (US) |
United States |
|
com.truist.mobile |
Truist Mobile - Banking Made Better |
United States |
|
com.usaa.mobile.android.usaa |
USAA Mobile |
United States |
|
com.usbank.mobilebanking |
U.S. Bank - Inspired by customers |
United States |
|
com.wf.wellsfargomobile |
Wells Fargo Mobile |
United States |
|
com.woodforest |
Woodforest Mobile Banking |
United States |
|
com.zellepay.zelle |
Zelle |
United States |
|
es.liberbank.cajasturapp |
Banca Digital Liberbank |
United States |
|
org.ncsecu.mobile |
SECU |
United States |
|
com.key.android |
KeyBank Mobile |
United States |
|
com.regions.mobbanking |
Regions Bank |
United States |
|
com.clairmail.fth |
Fifth Third Mobile Banking |
United States |
|
com.plunien.poloniex |
Poloniex Crypto Exchange |
Crypto |
|
com.wallet.crypto.trustapp |
Trust: Crypto & Bitcoin Wallet |
Crypto |
|
com.binance.dev |
Binance - Buy & Sell Bitcoin Securely |
Crypto |
|
com.coinbase.android |
Coinbase – Buy & Sell Bitcoin. Crypto Wallet |
Crypto |
|
com.kraken.trade |
Pro: Advanced Bitcoin & Crypto Trading |
Crypto |
|
io.metamask |
MetaMask - Buy, Send and Swap Crypto |
Crypto |
|
net.bitbay.bitcoin |
Bitcoin & Crypto Exchange - BitBay |
Crypto |
|
net.bitstamp.app |
Bitstamp – Buy & Sell Bitcoin at Crypto Exchange |
Crypto |
|
piuk.blockchain.android |
Blockchain Wallet. Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum |
Crypto |
|
com.latuabancaperandroid |
Intesa Sanpaolo Mobile |
Italy |
|
com.lynxspa.bancopopolare |
YouApp |
Italy |
|
com.sella.BancaSella |
Banca Sella |
Italy |
|
it.bcc.iccrea.mycartabcc |
myCartaBCC |
Italy |
|
it.bnl.apps.banking |
BNL |
Italy |
|
it.carige |
Carige Mobile |
Italy |
|
it.copergmps.rt.pf.android.sp.bmps |
Banca MPS |
Italy |
|
it.creval.bancaperta |
Bancaperta |
Italy |
|
it.nogood.container |
UBI Banca |
Italy |
|
it.popso.SCRIGNOapp |
SCRIGNOapp |
Italy |
|
posteitaliane.posteapp.appbpol |
BancoPosta |
Italy |
|
posteitaliane.posteapp.apppostepay |
Postepay |
Italy |
|
ca.mobile.explorer |
CA Mobile |
Portugal |
|
cgd.pt.caixadirectaparticulares |
Caixadirecta |
Portugal |
|
com.abanca.bm.pt |
ABANCA - Portugal |
Portugal |
|
com.bbva.mobile.pt |
BBVA Portugal |
Portugal |
|
com.exictos.mbanka.bic |
Banco BIC, SA |
Portugal |
|
pt.bancobpi.mobile.fiabilizacao |
BPI APP |
Portugal |
|
pt.novobanco.nbapp |
NB smart app |
Portugal |
|
pt.santandertotta.mobileparticulares |
Santander Particulares |
Portugal |
|
pt.sibs.android.mbway |
MB WAY |
Portugal |
|
wit.android.bcpBankingApp.activoBank |
ActivoBank |
Portugal |
|
wit.android.bcpBankingApp.millennium |
Millenniumbcp |
Portugal |
|
app.wizink.es |
WiZink, tu banco senZillo |
Spain |
|
com.bankinter.launcher |
Bankinter Móvil |
Spain |
|
com.bbva.bbvacontigo |
BBVA Spain |
Spain |
|
com.cajasur.android |
Cajasur |
Spain |
|
com.db.pbc.mibanco |
Mi Banco db |
Spain |
|
com.grupocajamar.wefferent |
Grupo Cajamar |
Spain |
|
com.imaginbank.app |
imaginBank - Your mobile bank |
Spain |
|
com.indra.itecban.mobile.novobanco |
NBapp Spain |
Spain |
|
com.indra.itecban.triodosbank.mobile.banking |
Triodos Bank. Banca Móvil |
Spain |
|
com.mediolanum |
Banco Mediolanum España |
Spain |
|
com.rsi |
ruralvía |
Spain |
|
com.targoes_prod.bad |
TARGOBANK - Banca a distancia |
Spain |
|
com.tecnocom.cajalaboral |
Banca Móvil Laboral Kutxa |
Spain |
|
es.bancosantander.apps |
Santander |
Spain |
|
es.caixagalicia.activamovil |
ABANCA- Banca Móvil |
Spain |
|
es.caixaontinyent.caixaontinyentapp |
Caixa Ontinyent |
Spain |
|
es.cecabank.ealia2103appstore |
UniPay Unicaja |
Spain |
|
es.cm.android |
Bankia |
Spain |
|
es.evobanco.bancamovil |
EVO Banco móvil |
Spain |
|
es.ibercaja.ibercajaapp |
Ibercaja |
Spain |
|
es.lacaixa.mobile.android.newwapicon |
CaixaBank |
Spain |
|
es.openbank.mobile |
Openbank – banca móvil |
Spain |
|
es.pibank.customers |
Pibank |
Spain |
|
es.univia.unicajamovil |
UnicajaMovil |
Spain |
|
www.ingdirect.nativeframe |
ING España. Banca Móvil |
Spain |
|
be.argenta.bankieren |
Argenta Banking |
Belgium |
|
be.axa.mobilebanking |
Mobile Banking Service |
Belgium |
|
be.belfius.directmobile.android |
Belfius Mobile |
Belgium |
|
com.bnpp.easybanking |
Easy Banking App |
Belgium |
|
com.ing.banking |
ING Banking |
Belgium |
|
com.kbc.mobile.android.phone.kbc |
KBC Mobile |
Belgium |
|
ca.affinitycu.mobile |
Affinity Mobile |
Canada |
|
ca.bnc.android |
National Bank of Canada |
Canada |
|
ca.hsbc.hsbccanada |
HSBC Canada |
Canada |
|
ca.manulife.MobileGBRS |
Manulife Mobile |
Canada |
|
ca.motusbank.mapp |
motusbank mobile banking |
Canada |
|
ca.pcfinancial.bank |
PC Financial Mobile |
Canada |
|
ca.servus.mbanking |
Servus Mobile Banking |
Canada |
|
ca.tangerine.clients.banking.app |
Tangerine Mobile Banking |
Canada |
|
com.atb.ATBMobile |
ATB Personal - Mobile Banking |
Canada |
|
com.cibc.android.mobi |
CIBC Mobile Banking® |
Canada |
|
com.coastcapitalsavings.dcu |
Coast Capital Savings |
Canada |
|
com.desjardins.mobile |
Desjardins mobile services |
Canada |
|
com.eqbank.eqbank |
EQ Bank Mobile Banking |
Canada |
|
com.meridian.android |
Meridian Mobile Banking |
Canada |
|
com.pcfinancial.mobile |
Simplii Financial |
Canada |
|
com.rbc.mobile.android |
RBC Mobile |
Canada |
|
com.shaketh |
Shakepay: Buy Bitcoin Canada |
Canada |
|
com.td |
TD Canada |
Canada |