Xenomorph: A newly hatched Banking Trojan
15 February 2022

Jump to
Intro
In February 2022, ThreatFabric came across a new Android banking Trojan, which we dubbed Xenomorph. The name comes from its clear ties with another infamous banking Trojan, Alien, from which Xenomorph adopts class names and interesting strings.
Based on the intelligence gathered, users of 56 different European banks are among the targets of this new Android malware trojan, distributed on the official Google Play Store, with more than 50.000 installations.
Just like the monster protagonist of the famous Ridley Scott’s franchise, this malware shares some aspects with its predecessor. However, despite its obvious ties to one of the most wide-spread malware of the last two years, Xenomorph is radically different from Alien in functionalities. This fact, in addition to the presence of not implemented features and the large amount of logging present on the malware, may suggest that this malware might be the in-progress new project of either the actors responsible with the original Alien, or at least of someone familiar with its code base. However, this is only speculation at the moment.
Distribution
As we have previously discussed, threat actors are increasingly focusing their efforts into sneaking their way onto the Google Play Store (MITRE T1475).
Google has seemingly taken some action to reduce the amount of malicious applications on the app market, but often these efforts are not enough to stop criminals from reaching the store. As part of our daily threat hunting, ThreatFabric analysts encounter and report malicious applications on the store to Google.
One of the applications ThreatFabric discovered was posing as “Fast Cleaner”, an application aiming at speeding up the device by removing unused clutter and removing battery optimization blocks. The application itself seemed successful, with more than 50.000 installations reported on Google Play. This is not an uncommon lure, and we have seen malware families like Vultur and Alien being deployed by such application.

Upon analysis, we recognized this application as belonging to the Gymdrop dropper family. Gymdrop is a dropper family discovered by ThreatFabric in November 2021. Previously it was observed deploying a Alien.A payload. From the configuration downloaded by the dropper, ThreatFabric was able to confirm that this dropper family continues to adopt this malware family as its payload. However, contrary to the past, the server hosting the malicious code also contained two other malware families, which were also returned instead of Alien, based on specific triggers.
Firstly, we observed samples belonging to a new wave of ExobotCompact.D, which has been living a new resurgence in the past few weeks, posing as Google play store applications, as well as different banking applications.
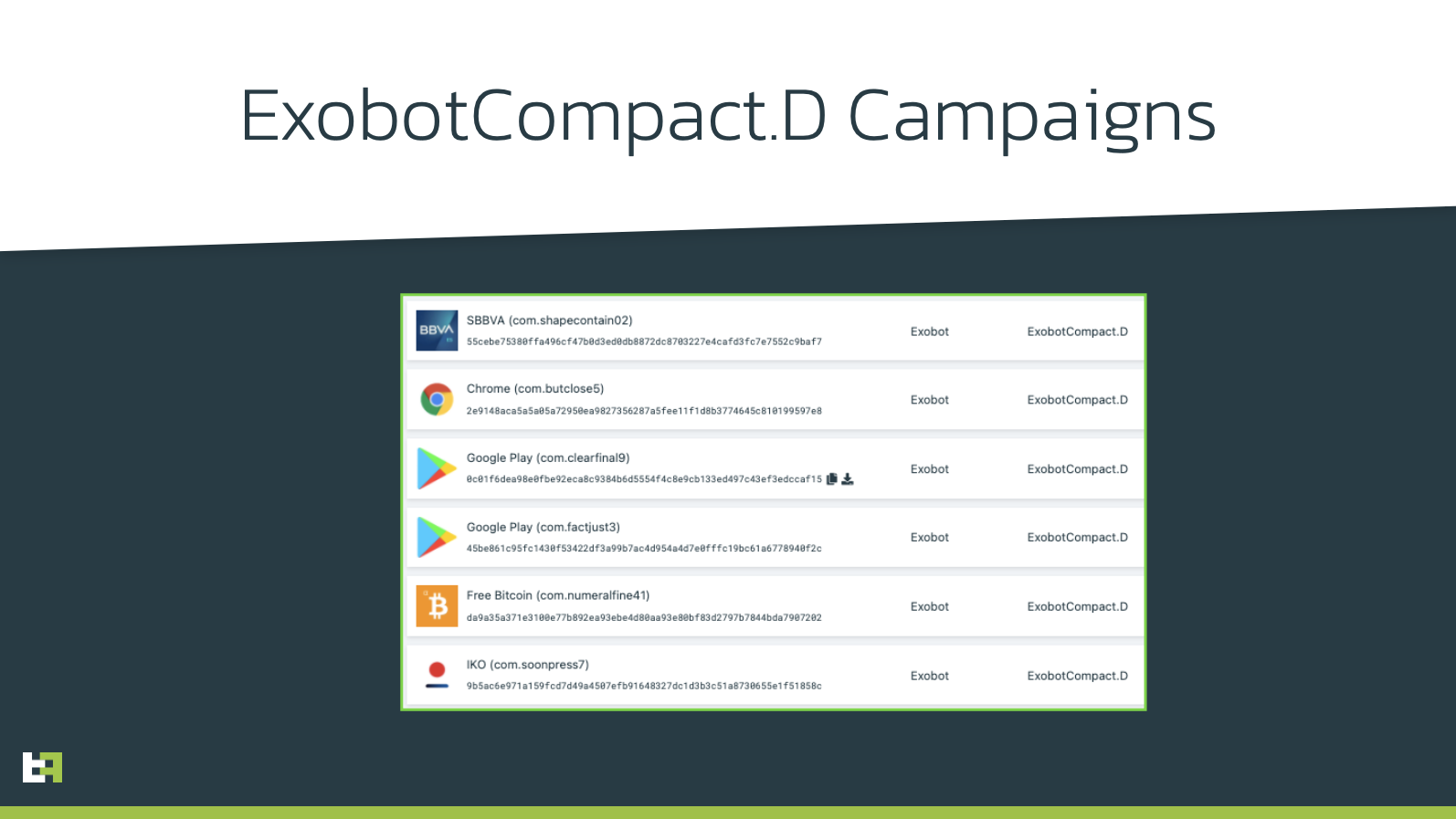
However, despite being the first time we observed ExobotCompact.D and Alien.A being distributed by the same dropper infrastructure, what surprised us the most was the presence of a totally new malware family. This is how ThreatFabric discovered Xenomorph.
Capabilities
Here is a comprehensive list of Xenomorph capabilities:
Accessibility Services
This Android Banking malware is heavily under development, and mostly supports the minimum list of features required for a modern Android banking trojan. As discussed before, its main attack vector is the use of the overlay attack to steal credentials, combined with the use of SMS and Notification interception to log and use potential 2FA tokens.
The Accessibility engine powering this malware, together with the infrastructure and C2 protocol, are carefully designed to be scalable and updatable.
The information stored by the logging capability of this malware is very extensive, and if sent back to the C2 server, could be used to implement keylogging, as well as collecting behavioural data on victims and on installed applications, even if they are not part of the list of targets.
int v0 = arg4.getEventType();
switch (v0) {
case 1: {
UtilGlobal.Log("onAccessibilityEvent", "### type: TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED");
break;
}
case 2: {
UtilGlobal.Log("onAccessibilityEvent", "### type: TYPE_VIEW_LONG_CLICKED");
break;
}
case 4: {
UtilGlobal.Log("onAccessibilityEvent", "### type: TYPE_VIEW_SELECTED");
break;
}
case 8: {
UtilGlobal.Log("onAccessibilityEvent", "### type: TYPE_VIEW_FOCUSED");
break;
}
...
case 0x20: {
UtilGlobal.Log("onAccessibilityEvent", "### type: TYPE_WINDOW_STATE_CHANGED");
this.windowStateChangedEvent(arg4); // function responsible for injections
break;
}
case 0x40: {
UtilGlobal.Log("onAccessibilityEvent", "### type: TYPE_NOTIFICATION_STATE_CHANGED");
this.notificationStateChanged(arg4); // function responsible for logging notifications
break;
}
...
}
Xenomorph seems to be in its inphancy stage, based on the fact that many commands are present in the code of the malware, but are not implemented. In addition to this, the large amount of logging used also suggests that this might be a in-progress malware project.
Despite having so far a “in-progress” amount of features, Xenomorph contains code to support much more. Its Accessibility Engine is very detailed, and is designed with a modular approach in mind. It contains modules for each specific action required by the bot, and can be easily extended to support more functionalities. It would be unsurprising to see this bot sport semi-ATS capabilities in the very near future.
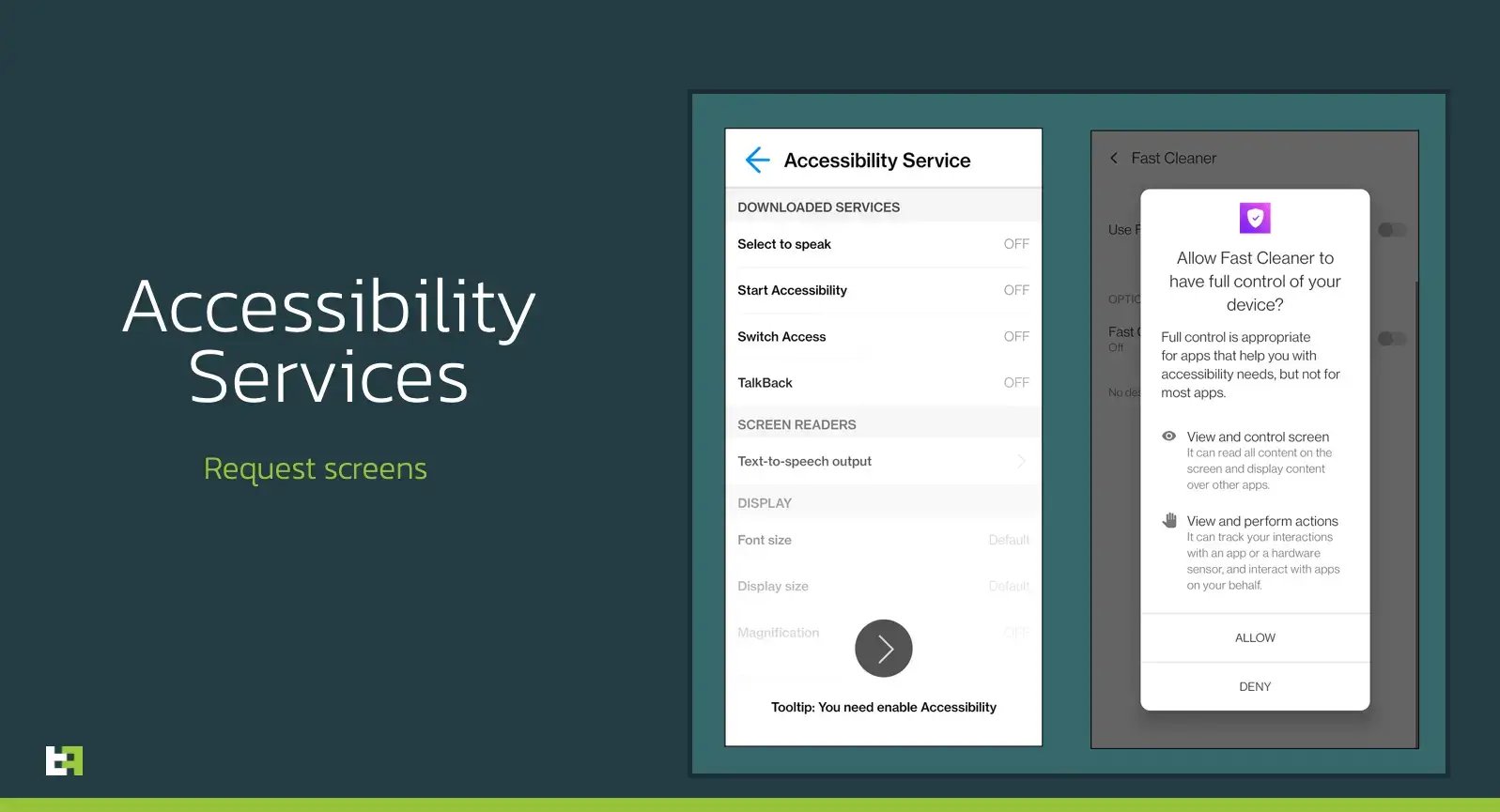
Like many other Android Banking trojans, this trojan heavily relies on the overlay attack mechanism to fool its victims into revealing Personal Identifiable Information (PII), which could then be used by criminals to perform fraud. If the malware obtains the Accessiblity Services privileges, which it insistently requests after being started, it will automatically grant itself all the requires permissions and then silently execute on the device.
Here are some screenshots of the request screens:
Modus Operandi
The main attack vector for Xenomorph is the classic overlay attack powered by Accessibility Services privileges. Once the malware is up and running on a device, its background services receive accessibilty events whenever something new happens on the device. if the application opened is part of the list of targets, then Xenomorph will trigger an overlay injection and show a WebView Activity posing as the targeted package. Here as a few examples of triggered overlays:
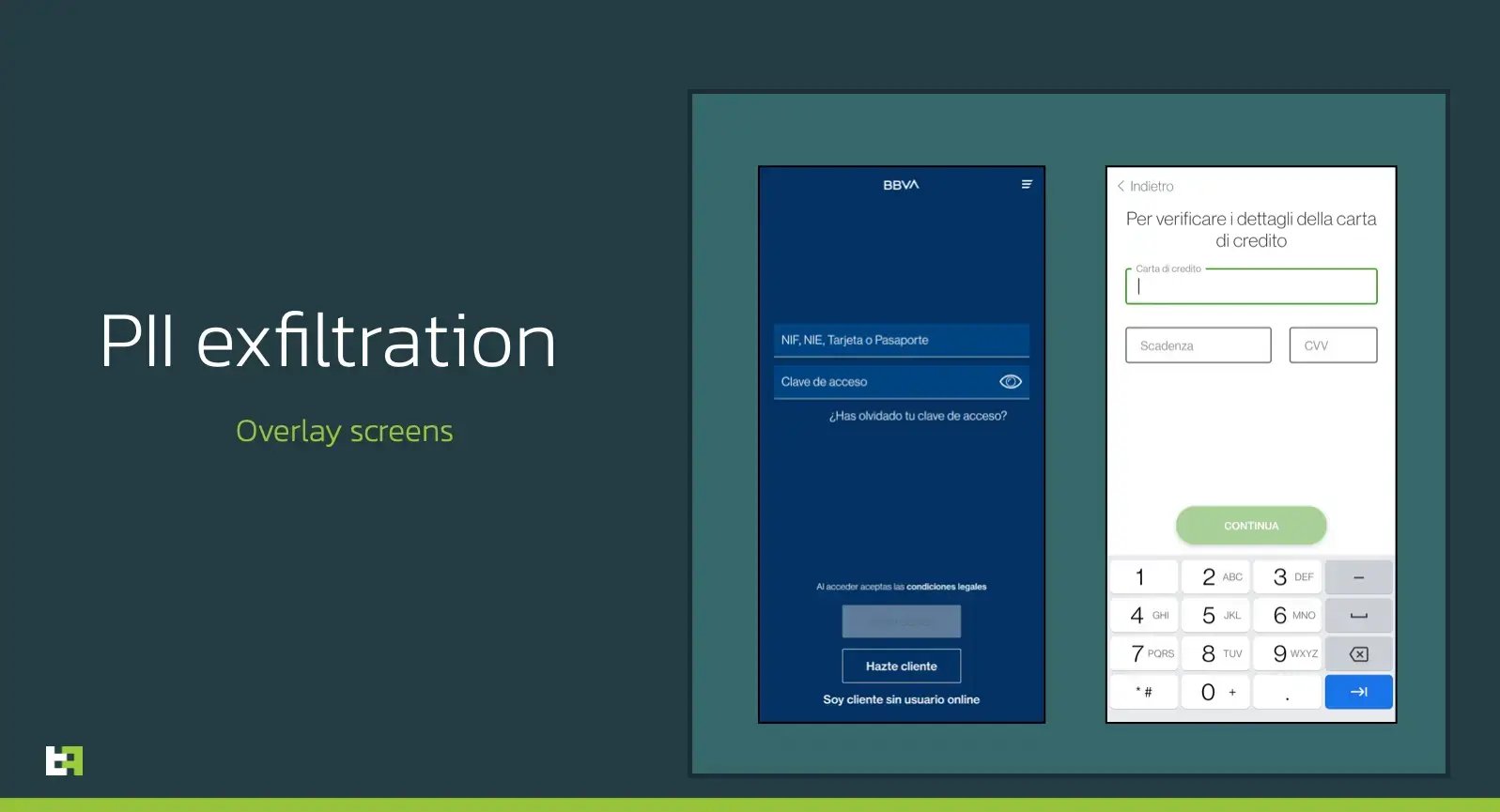
This feature is performed by the code you see in the snippet underneath:
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
this.context = this;
OverlayInjectResource v0 = UtilGlobal.getPackageInjection(this, UtilGlobal.SettingsRead(this, "AITG"));
this.resource = v0;
this.hideStop = true;
if (!this.stopActivity && v0 != null) {
try {
WebView v0_2 = new WebView(this);
this.wv = v0_2;
v0_2.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
this.wv.setScrollBarStyle(0);
this.wv.setWebViewClient(new MyWebViewClient(null));
this.wv.setWebChromeClient(new MyWebChromeClient(null));
this.wv.addJavascriptInterface(new WebAppInterface(this), "Android");
String v3 = this.resource.getPageResource(this);
this.wv.loadDataWithBaseURL(null, v3, "text/html", "UTF-8", null);
this.setContentView(this.wv);
} catch (Exception v0_1) {
v0_1.printStackTrace();
}
return;
}
}
In addition, the malware is able to abuse Accessibility Services to log everything that happens on the device. At the moment of writing, all the information gathered is only displayed on the local device logs, but in the future a very minor modification would be enough to add keylogging and Accessibility logging capabilities to the malware.
Targets
As a first step, the malware sends back the list of installed packages on device, and based on what targeted application is present on the device, it downloads the corresponding overlays to inject. The list of overlay targets returned by Xenomorph includes targets from Spain, Portugal, Italy, and Belgium, as well as some general purpose applications like emailing services, and cryptocurrency wallets.

C2 Communication & Commands
For its C2 communication, Xenomorph relies on the open-source project Retrofit2.
Retrofit is a type-safe REST client for Android, Java and Kotlin developed by Square. The library provides a powerful framework for authenticating and interacting with APIs and sending network requests with OkHttp.
NOTE : ThreatFabric wants to explicitly mention that RetroFit is a legitimate and legal product. The developers that created this project have no control over the misuse of their software.
After obtaining Accessibility Services privileges, Xenomorph will first register and verify itself with the C2, by sending a request containing the following information at the endpoint ‘ping’:
{
"api": "%DEVICE_SDK_NUMBER%",
"apps": ["%LIST%", "%OF%", "%INSTALLED%", "%APPS%"],
"imei": "%IMEI%",
"model": "%MODEL%",
"numbers": ["%LIST%", "%OF%", "%CONTACTS%"],
"tag": "%BOT_TAG%",
"uid": "%UID%"
}The messages are encrypted with an ever changing AES key and IV, together with an hash of the message to ensure the integrity of the communication. The first message sent to the C2 has the following format and uses an hardcoded testKey. The initial information exfiltrated about the device and displayed above is contained in the tag ‘id’:
{
"hash": "%BASE64_ENCODED_SHA256%",
"id": "%ENCRYPTED_DATA%",
"iv": "%IV_FOR_AES%",
"type": "request_verify"
}Following this exchange, the bot can be successfully registered and communicate with the C2. In this stage, the malware will periodically poll for new commands from the C2, receiving the following response:
{
"type": "get_coms",
"coms": ["<COMMANDS>"]
}The value of ‘coms’ can be empty, or it can be any of the values described in the following section.
Commands
The following table contains all the accepted commands that can be sent from the C2:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| sms_log | Log SMS |
| notif_ic_disable | Disable Intercept notification |
| inj_list | List injects |
| notif_ic_enable | Enable notification intercept |
| sms_ic_disable | Disable SMS intercept |
| inj_enable | Enable Injects |
| app_list | Get installed apps list |
| sms_ic_enable | Enable SMS intercept |
| inj_update | Update list of injects |
| inj_disable | Disable injects |
| sms_ic_update | Not implemented |
| sms_ic_list | Not implemented |
| notif_ic_list | Not implemented |
| self_cleanup | Not implemented |
| notif_ic_update | Not implemented |
| fg_disable | Not implemented |
| fg_enable | Not implemented |
| app_kill | Not implemented |
Endpoints
Here is a list of the endpoints used by Xenomorph to communicate with its C2
| Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|
| /ping | Used for initial verification step |
| /metrics | Used to retrieve commands from the c2 and send exfiltrated information |
Similarities with Alien
Both choices of having a fully modular Accessibility Service engine and the use of Retrofit2 could remind of another powerful Android Banking trojan, S.O.V.A.. However, despite this design similarities, the two families are completely different in implementation. On the other hand, there are many similarities with another Android Banking Trojan, which has been around for more than 2 years now: Alien.
The first similarity between these two families is the use of the same HTML resource page to trick victims into granting the Accessibility Services privileges, which however has been re-used by many families before Xenomorph.
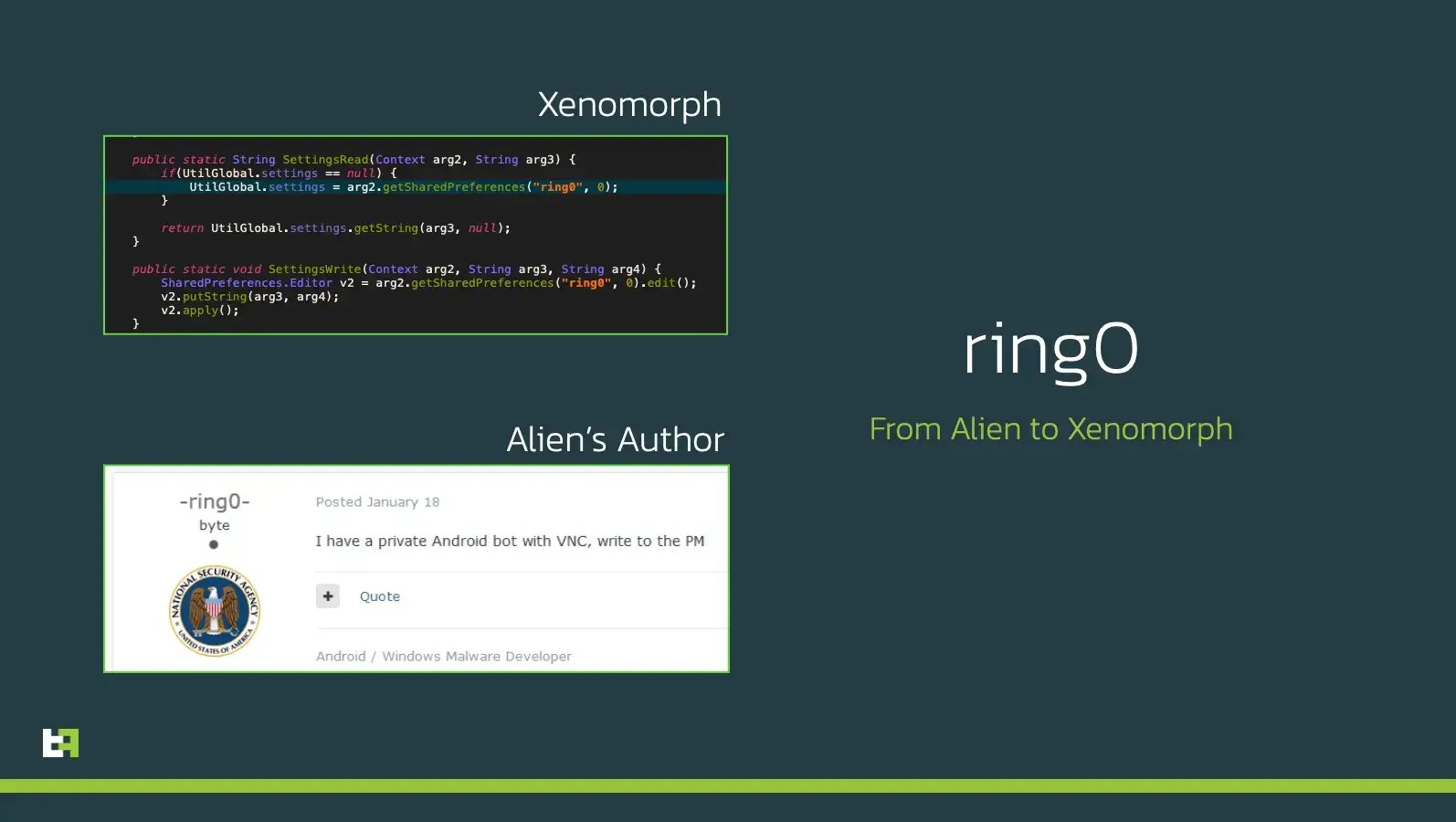
This new malware also uses a very similar style of state-tracking through the use of the ‘SharedPreferences’ file. This file is commonly used to track the state of an application. However, the style of variable naming used by Xenomorph is very reminiscent of Alien, despite being potentially even more detailed.
Potentially the most interesting fact is the actual name of the sharedPreferences file used to store the configuration for Xenomorph: the file is named ring0.xml.
This might look like any other generic random string, but it happens to coincide with the name of the supposed actor behind the development of the original Alien malware.
If this could look like a coincidence, there are many occurences of very peculiar logging strings and class names observed first in Cerberus, and later in its successor Alien.

Currently the set of capabilities of Alien is much larger than the one of Xenomorph. However, considering that this new malware is still very young and adopts a strong modular design, it is not hard to predict new features coming in the near future.
Conclusions
The surfacing of Xenomorph shows, once again, that threat actors are focusing their attention on landing applications on official markets. This is also a signal that the underground market for droppers and distribution actors has increased its activity, considering that we just very recently observed Medusa and Cabassous also being distributed side-by-side.
Xenomorph currently is an average Android Banking Trojan, with a lot of untapped potential, which could be released very soon. Modern Banking malware is evolving at a very fast rate, and criminals are starting to adopt more refined development practices to support future updates. Xenomorph is at the forefront of this change.
The current version of Xenomorph is capable of abusing Accessibility Services to steal PII from unaware victims, prevent uninstallation and intercept SMS and notifications. ThreatFabric predicts that with some more time to finish development, this malware could reach higher threat levels, comparable to other modern Android Banking trojans.
MTI & CSD
This and other mobile malware is tracked in our Mobile Threat Intel service (MTI). Try out our MTI feed today! Send a message to sales@threatfabric.com, and get 30 days access to our portal free of charge.
If you want more information on how we detect mobile malware on mobile devices, you can directly contact us at: info@threatfabric.com
Appendix
Xenomorph Samples
| App name | Package name | SHA-256 |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Cleaner | com.census.turkey | 64c0f71d9c903f7b22a193a7844ea98a5f9db62b4dcc139f75f6d9698645f369 |
| Fast Cleaner | com.laundry.vessel | 76e9359cfa98bb326f544577394b007132db63fd19fedde73a76162744b93c6f |
| Fast Cleaner | com.tip.equip | 2d6f26c16d29d4e68ece44e3ac558cd557d906684ee1a546ea982e7a64ddf0ce |
| Fast Cleaner | com.spike.old | 2877b27f1b6c7db466351618dda4f05d6a15e9a26028f3fc064fa144ec3a1850 |
Xenomorph C2
| C2 | Description |
|---|---|
| simpleyo5[.]tk | Main C2 |
| simpleyo5[.]cf | Backup C2 |
| art12sec[.]ga | Backup C2 |
| kart12sec[.]gq | Backup C2 |
| homeandofficedeal[.]com | Overlay C2 |
Xenomorph Targets
| Package Name | App Name |
|---|---|
| ca.mobile.explorer | CA Mobile |
| cgd.pt.caixadirectaparticulares | Caixadirecta |
| com.abanca.bm.pt | ABANCA - Portugal |
| com.bbva.mobile.pt | BBVA Portugal |
| com.exictos.mbanka.bic | Banco BIC, SA |
| pt.bancobpi.mobile.fiabilizacao | BPI APP |
| pt.novobanco.nbapp | NB smart app |
| pt.sibs.android.mbway | MB WAY |
| wit.android.bcpBankingApp.millennium | Millenniumbcp |
| be.argenta.bankieren | Argenta Banking |
| be.axa.mobilebanking | Mobile Banking Service |
| be.belfius.directmobile.android | Belfius Mobile |
| com.beobank_prod.bad | Beobank Mobile |
| com.bnpp.easybanking | Easy Banking App |
| com.ing.banking | ING Banking |
| com.kbc.mobile.android.phone.kbc | KBC Mobile |
| com.binance.dev | Binance - Buy & Sell Bitcoin Securely |
| com.bitfinex.mobileapp | Bitfinex |
| com.coinbase.android | Coinbase – Buy & Sell Bitcoin. Crypto Wallet |
| com.kraken.trade | Pro: Advanced Bitcoin & Crypto Trading |
| com.plunien.poloniex | Poloniex Crypto Exchange |
| com.squareup.cash | Cash App |
| com.transferwise.android | TransferWise Money Transfer |
| com.wavesplatform.wallet | Waves.Exchange |
| net.bitbay.bitcoin | Bitcoin & Crypto Exchange - BitBay |
| net.bitstamp.app | Bitstamp – Buy & Sell Bitcoin at Crypto Exchange |
| org.electrum.electrum | Electrum Bitcoin Wallet |
| piuk.blockchain.android | Blockchain Wallet. Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum |
| app.wizink.es | WiZink, tu banco senZillo |
| com.bankinter.launcher | Bankinter Móvil |
| com.bbva.bbvacontigo | BBVA Spain |
| com.bbva.netcash | BBVA Net Cash ES & PT |
| com.cajasur.android | Cajasur |
| com.db.pbc.mibanco | Mi Banco db |
| com.grupocajamar.wefferent | Grupo Cajamar |
| com.imaginbank.app | imaginBank - Your mobile bank |
| com.indra.itecban.mobile.novobanco | NBapp Spain |
| com.indra.itecban.triodosbank.mobile.banking | Triodos Bank. Banca Móvil |
| com.mediolanum | Banco Mediolanum España |
| com.rsi | ruralvía |
| com.targoes_prod.bad | TARGOBANK - Banca a distancia |
| com.tecnocom.cajalaboral | Banca Móvil Laboral Kutxa |
| es.bancosantander.apps | Santander |
| es.caixagalicia.activamovil | ABANCA- Banca Móvil |
| es.caixaontinyent.caixaontinyentapp | Caixa Ontinyent |
| es.cecabank.ealia2091appstore | ABANCA Pay - Paga y envía dinero con el móvil |
| es.cecabank.ealia2103appstore | UniPay Unicaja |
| es.cm.android | Bankia |
| es.evobanco.bancamovil | EVO Banco móvil |
| es.ibercaja.ibercajaapp | Ibercaja |
| es.lacaixa.mobile.android.newwapicon | CaixaBank |
| es.liberbank.cajasturapp | Banca Digital Liberbank |
| es.openbank.mobile | Openbank – banca móvil |
| es.pibank.customers | Pibank |
| es.univia.unicajamovil | UnicajaMovil |
| www.ingdirect.nativeframe | ING España. Banca Móvil |
| com.latuabancaperandroid | Intesa Sanpaolo Mobile |
| com.lynxspa.bancopopolare | YouApp |
| com.sella.BancaSella | Banca Sella |
| it.bcc.iccrea.mycartabcc | myCartaBCC |
| it.bnl.apps.banking | BNL |
| it.carige | Carige Mobile |
| it.copergmps.rt.pf.android.sp.bmps | Banca MPS |
| it.creval.bancaperta | Bancaperta |
| it.nogood.container | UBI Banca |
| it.popso.SCRIGNOapp | SCRIGNOapp |
| posteitaliane.posteapp.appbpol | BancoPosta |
| posteitaliane.posteapp.apppostepay | Postepay |
| com.android.vending | Google Play |
| com.connectivityapps.hotmail | Connect for Hotmail & Outlook: Mail and Calendar |
| com.google.android.gm | Gmail |
| com.mail.mobile.android.mail | mail.com mail |
| com.microsoft.office.outlook | Microsoft Outlook: Organize Your Email & Calendar |
| com.paypal.android.p2pmobile | PayPal Mobile Cash: Send and Request Money Fast |
| com.yahoo.mobile.client.android.mail | Yahoo Mail – Organized Email |